Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy
- PMID: 38004669
- PMCID: PMC10673056
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112657
Attenuated Replication-Competent Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing an ECM-Modifying Transgene Hyaluronan Synthase 2 of Naked Mole Rat in Oncolytic Gene Therapy
Abstract
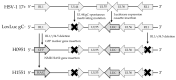
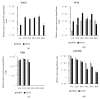
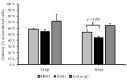
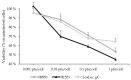
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) has proven successful in treating human cancer. Since the approval of talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC) in 2015, HSV has been thoroughly researched to discover novel mechanisms to combat cancer and treat other diseases. Another HSV-based drug, beremagene geperpavec (B-VEC), received approval in 2023 to treat the rare genetic disease dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, and was also the first clinically approved HSV vector carrying an extracellular matrix (ECM)-modifying transgene. The ECM is a network of macromolecules surrounding cells, which provides support and regulates cell growth and differentiation, the disruption of which is common in cancer. The naked mole rat (NMR) has a thick ECM and a unique mutation in the hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2) gene, which has been linked to the high cancer resistance of the species. To study the effect of this mutation in human cancer, we have developed an attenuated, replication-competent HSV vector expressing the NMR-HAS2 gene. The viral replication, transgene expression and cytotoxic effect of the novel vector was studied in glioma cells. Our results show that an attenuated, replication-competent HSV vector expressing a foreign ECM-modifying transgene, namely HAS2, provides an effective tool to study and combat cancer in humans.
Keywords: cancer; extracellular matrix; herpes simplex; hyaluronan synthase; naked mole rat; oncolytic virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyzes, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beremagene Geperpavec: First Approval.Drugs. 2023 Aug;83(12):1131-1135. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01921-5. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37432558 Review.
-
The Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Talimogene Laherparepvec Shows Promising Efficacy in Neuroendocrine Cancer Cell Lines.Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109(4):346-361. doi: 10.1159/000500159. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Neuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31280274
-
Engineering HSV-1 Vectors for Gene Therapy.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2060:73-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9814-2_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31617173
-
Positron emission tomography-based imaging of transgene expression mediated by replication-conditional, oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant vectors in vivo.Cancer Res. 2001 Apr 1;61(7):2983-95. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11306477
-
Oncolytic virus therapy using genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2060-4. doi: 10.2741/2823. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981691 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Potentials of Hyaluronic Acid-coated Polymeric Nanoparticles in Enhanced Cancer Treatment by Precision Drug Delivery, Tackling Drug Resistance, and Reshaping the Tumour Micro Environment.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(20):3960-3999. doi: 10.2174/0109298673302510240328050115. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38571347 Review.
References
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S., Garrigue A., Wang G.P., Soulier J., Lim A., Morillon E., Clappier E., Caccavelli L., Delabesse E., Beldjord K., et al. Insertional Oncogenesis in 4 Patients after Retrovirus-Mediated Gene Therapy of SCID-X1. J. Clin. Investig. 2008;118:3132–3142. doi: 10.1172/JCI35700. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu N., Watkins S.C., Schaffer P.A., DeLuca N.A. Prolonged Gene Expression and Cell Survival after Infection by a Herpes Simplex Virus Mutant Defective in the Immediate-Early Genes Encoding ICP4, ICP27, and ICP22. J. Virol. 1996;70:6358–6369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.9.6358-6369.1996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

