The Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I-Enriched Diet on the Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Queen Scallop (Aequipecten opercularis Linnaeus, 1758) Extracts
- PMID: 38004734
- PMCID: PMC10673489
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112723
The Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I-Enriched Diet on the Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Queen Scallop (Aequipecten opercularis Linnaeus, 1758) Extracts
Abstract
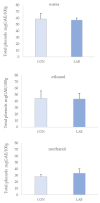
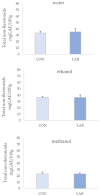
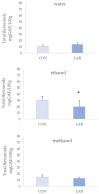
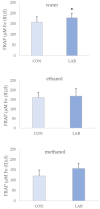
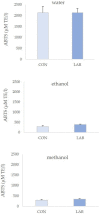
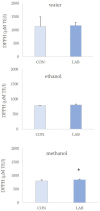
The use of probiotics in the diet of bivalves poses a great potential in aquaculture as an alternative to antibiotics. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I on the phenolic content and antioxidant capacity (AC) of queen scallop extracts after one month of feeding. Total phenols (TP) ranged from 28.17 ± 3.11 to 58.58 ± 8.57 mg GAE/100 g, total non-flavonoids (TNF) from 23.33 ± 3.66 to 36.56 ± 9.91 mg GAE/100 g, and total flavonoids (TF) from 10.56 ± 5.57 to 30.16 ± 1.69 mg CE/100 g. AC was assessed via three different methods: the ferric-reducing ability of plasma assay (FRAP), 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic) acid assay (ABTS), and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl assay (DPPH). FRAP values ranged from 0.13 ± 0.03 to 0.17 ± 0.02 µM AA/g, ABTS from 0.68 ± 0.11 to 2.79 ± 0.34 µM AA/g, and DPPH from 1.75 ± 0.17 to 2.98 ± 0.53 µM AA/g. Among all extracts, the best phenolic content and AC were observed in water extracts from queen scallops. The bivalves treated with the Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I-enriched diet showed higher AC according to the FRAP assay in all extracts. A significant correlation was observed between AC and TP and TNF in control and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I-treated scallops.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum I; antioxidant capacity; phenolic content; probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro Antioxidant Activities and Polyphenol Contents of Seven Commercially Available Fruits.Pharmacognosy Res. 2016 Oct-Dec;8(4):258-264. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.188875. Pharmacognosy Res. 2016. PMID: 27695265 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of aerial parts of medicinal plant Coronopus didymus.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017 Aug;10(8):792-801. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.07.024. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017. PMID: 28942828
-
Antioxidant potential of two varieties of Sesamum indicum L. collected from Indonesia.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2018 Mar 10;13(3):211-218. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2018.02.004. eCollection 2018 Jun. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 31435326 Free PMC article.
-
LC-ESI-QTOF-MS2 Characterization of Phenolic Compounds in Different Lentil (Lens culinaris M.) Samples and Their Antioxidant Capacity.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 3;28(3):44. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2803044. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37005759
-
Polysaccharides, Total Phenolic, and Flavonoid Content from Different Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) Genotypes and Their Antioxidants and Antibacterial Properties.Plants (Basel). 2021 Sep 14;10(9):1900. doi: 10.3390/plants10091900. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34579432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saber S., Abd El-Fattah E.E., Yahya G., Gobba N.A., Maghmomeh A.O., Khodir A.E., Mourad A.A.E., Saad A.S., Mohammed H.G., Nouh N.A., et al. A Novel Combination Therapy Using Rosuvastatin and Lactobacillus Combats Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats by Targeting the TXNIP/NLRP3 Interaction and Influencing Gut Microbiome Composition. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:341. doi: 10.3390/ph14040341. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iorizzo M., Albanese G., Letizia F., Testa B., Tremonte P., Vergalito F., Lombardi S.J., Succi M., Coppola R., Sorrentino E. Probiotic Potentiality from Versatile Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains as Resource to Enhance Freshwater Fish Health. Microorganisms. 2022;10:463. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

