Aquiluscidin, a Cathelicidin from Crotalus aquilus, and the Vcn-23 Derivative Peptide, Have Anti-Microbial Activity against Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria
- PMID: 38004789
- PMCID: PMC10673557
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112778
Aquiluscidin, a Cathelicidin from Crotalus aquilus, and the Vcn-23 Derivative Peptide, Have Anti-Microbial Activity against Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria
Abstract
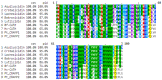
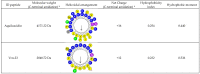
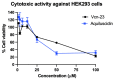
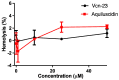
Anti-microbial peptides play a vital role in the defense mechanisms of various organisms performing functions that range from the elimination of microorganisms, through diverse mechanisms, to the modulation of the immune response, providing protection to the host. Among these peptides, cathelicidins, a well-studied family of anti-microbial peptides, are found in various animal species, including reptiles. Due to the rise in anti-microbial resistance, these compounds have been suggested as potential candidates for developing new drugs. In this study, we identified and characterized a cathelicidin-like peptide called Aquiluscidin (Aq-CATH) from transcripts obtained from the skin and oral mucosa of the Querétaro's dark rattlesnake, Crotalus aquilus. The cDNA was cloned, sequenced, and yielded a 566-base-pair sequence. Using bioinformatics, we predicted that the peptide precursor contains a signal peptide, a 101-amino-acid conserved cathelin domain, an anionic region, and a 34-amino-acid mature peptide in the C-terminal region. Aq-CATH and a derived 23-amino-acid peptide (Vcn-23) were synthesized, and their anti-microbial activity was evaluated against various species of bacteria in in vitro assays. The minimal inhibitory concentrations against bacteria ranged from 2 to 8 μg/mL for both peptides. Furthermore, at concentrations of up to 50 μM, they exhibited no significant hemolytic activity (<2.3% and <1.2% for Aquiluscidin and Vcn-23, respectively) against rat erythrocytes and displayed no significant cytotoxic activity at low concentrations (>65% cell viability at 25 µM). Finally, this study represents the first identification of an antimicrobial peptide in Crotalus aquilus, which belongs to the cathelicidin family and exhibits the characteristic features of these peptides. Both Aq-CATH and its derived molecule, Vcn-23, displayed remarkable inhibitory activity against all tested bacteria, highlighting their potential as promising candidates for further antimicrobial research.
Keywords: Crotalus aquilus; Gram-negative bacteria; Gram-positive bacteria; anti-microbial peptide; cathelicidin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiparasitic Evaluation of Aquiluscidin, a Cathelicidin Obtained from Crotalus aquilus, and the Vcn-23 Derivative Peptide against Babesia bovis, B. bigemina and B. ovata.Pathogens. 2024 Jun 10;13(6):496. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060496. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38921794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the first Crocodylus siamensis cathelicidin gene and RN15 peptide derived from cathelin domain exhibiting antibacterial activity.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019 Mar;66(2):142-152. doi: 10.1002/bab.1709. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30414293
-
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide from Alligator mississippiensis has antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumanii and Klebsiella pneumoniae.Dev Comp Immunol. 2017 May;70:135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2017.01.011. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Dev Comp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28089718
-
The cathelicidins--structure, function and evolution.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005 Feb;6(1):23-34. doi: 10.2174/1389203053027520. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005. PMID: 15638766 Review.
-
[Progress in cathelicidins antimicrobial peptides research].Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2012 Oct;33(5):523-6. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1141.2012.05523. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2012. PMID: 23019035 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Prokaryotic Expression, Purification, and Biological Properties of a Novel Bioactive Protein (PFAP-1) from Pinctada fucata.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 27;22(8):345. doi: 10.3390/md22080345. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195461 Free PMC article.
-
Cathelicidins: Opportunities and Challenges in Skin Therapeutics and Clinical Translation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;14(1):1. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010001. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39858288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiparasitic Evaluation of Aquiluscidin, a Cathelicidin Obtained from Crotalus aquilus, and the Vcn-23 Derivative Peptide against Babesia bovis, B. bigemina and B. ovata.Pathogens. 2024 Jun 10;13(6):496. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060496. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38921794 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Peptides in Overcoming Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Molecules. 2024 Dec 31;30(1):128. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010128. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Anti-Microbial Resistance. 2016. [(accessed on 1 April 2019)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resist....
-
- O’Neill J. Review on Anti-Microbial Resistance Anti-Microbial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. London: Review on Anti-Microbial Resistance. 2014. [(accessed on 3 May 2023)]. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20-%20Ta....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

