Effect of L. crispatus M247 Administration on Pregnancy Outcomes in Women Undergoing IVF: A Controlled, Retrospective, Observational, and Open-Label Study
- PMID: 38004807
- PMCID: PMC10673025
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112796
Effect of L. crispatus M247 Administration on Pregnancy Outcomes in Women Undergoing IVF: A Controlled, Retrospective, Observational, and Open-Label Study
Abstract
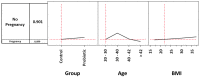
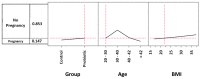
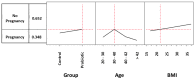
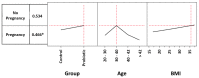
The aim of our study was to retrospectively evaluate whether the oral administration of L. crispatus (M247) could increase pregnancy and live birth rates in women undergoing assisted reproductive technology procedures. Enrolled women (N = 160) were divided into two groups: treated (N = 80) or untreated (N = 80) with the probiotic strain. The odds ratio (OR) for a treated woman to have a clinical pregnancy (CP) was 1.56. In women aged 30-40 years, M247 increased the probability of a CP in correlation with the progressive rise in BMI, reaching 47% (35% in controls) with a BMI of 35 (OR: 2.00). The CAID statistics showed that in a woman of the blastocyst subgroup, below 43 years, with a BMI over 18.6, treatment with M247 increased the chance of a CP from 28.4% to 44.5% (OR: 2.08; p < 0.05). Considering live births, the rate of the probiotic group was 12.5% versus 7.5% (OR: 1.76). Considering only the blastocyst subgroup, the treatment increased the number of live births by 200% (OR: 3.64; p = 0.05). As confirmed also by statistical indices NNT, NNH, and LHH, the use of M247 demonstrated a risk-benefit ratio to the full advantage of the benefits.
Keywords: ART; D3 embryos; D5 blastocysts; FIVET; ICSI; vaginal microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
F.D.P. is a board member of Pharmextracta. A.B. and M.C. are Pharmextracta consultants. The other authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The vaginal microbiome as a predictor for outcome of in vitro fertilization with or without intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a prospective study.Hum Reprod. 2019 Jun 4;34(6):1042-1054. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez065. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31119299
-
Leave the past behind: women's reproductive history shows no association with blastocysts' euploidy and limited association with live birth rates after euploid embryo transfers.Hum Reprod. 2021 Mar 18;36(4):929-940. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab014. Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33608730
-
Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (abnormal number of chromosomes) in in vitro fertilisation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 8;9(9):CD005291. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005291.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32898291 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus crispatus M247 oral administration: Is it really an effective strategy in the management of papillomavirus-infected women?Infect Agent Cancer. 2022 Oct 21;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00465-9. Infect Agent Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36271433 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for the number of embryos to transfer following in vitro fertilization No. 182, September 2006.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008 Aug;102(2):203-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.01.007. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008. PMID: 18773532 Review.
Cited by
-
The Safety of Probiotics Intended for Use in Pregnant and Lactating Women: From a Desirable to a Required Task.Foods. 2024 Dec 12;13(24):4024. doi: 10.3390/foods13244024. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39766967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Female genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction.Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024 Dec 4;46:e-rbgo82. doi: 10.61622/rbgo/2024rbgo82. eCollection 2024. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 39669302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligilactobacillus salivarius CECT5713 Increases Term Pregnancies in Women with Infertility of Unknown Origin: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2025 May 29;17(11):1860. doi: 10.3390/nu17111860. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The activity of cell-free supernatant of Lactobacillus crispatus M247: a promising treatment against vaginal infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 11;15:1586442. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1586442. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40568705 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Lactobacillus crispatus for Chronic Endometritis: A Comprehensive Clinical Trial and Experimental Investigation.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10349-6. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39172215
References
-
- WHO ICD-11. 2020. [(accessed on 11 November 2023)]. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/123700....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

