Rapid Detection and Quantification of Viable Cells of Pectobacterium brasiliense Using Propidium Monoazide Combined with Real-Time PCR
- PMID: 38004819
- PMCID: PMC10673545
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11112808
Rapid Detection and Quantification of Viable Cells of Pectobacterium brasiliense Using Propidium Monoazide Combined with Real-Time PCR
Abstract
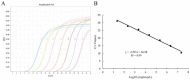
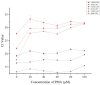
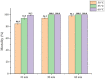
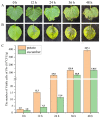
Pectobacterium brasiliense (Pbr) has caused significant economic losses in major vegetable production areas in Northern China by causing bacterial soft rot in cash crops such as potatoes and cucumbers. This study aimed to establish a PMA-qPCR detection method for Pbr by screening specific and sensitive primers based on the glu gene and the conserved region of the 23S rRNA gene. Based on the optimized PMA pretreatment conditions, a standard curve was designed and constructed for PMA-qPCR detection (y = -3.391x + 36.28; R2 = 0.99). The amplification efficiency reached 97%, and the lowest detection limit of viable cells was approximately 2 × 102 CFU·mL-1. The feasibility of the PMA-qPCR method was confirmed through a manually simulated viable/dead cell assay under various concentrations. The analysis of potato tubers and cucumber seeds revealed that nine naturally collected seed samples contained a range from 102 to 104 CFU·g-1 viable Pbr bacteria. Furthermore, the system effectively identified changes in the number of pathogenic bacteria in cucumber and potato leaves affected by soft rot throughout the disease period. Overall, the detection and prevention of bacterial soft rot caused by Pbr is crucial.
Keywords: PMA-qPCR; Pectobacterium brasiliense; bacterial soft rot; detection; viable cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Degefu Y. Co-occurrence of latent Dickeya and Pectobacterium species in potato seed tuber samples from northern Finland: Co-colonization of latent Dickeya and Pectobacterium species in potato seed lots. Agric. Food Sci. 2021;30:1–7. doi: 10.23986/afsci.101446. - DOI
-
- Merwe J.J.V.D., Coutinho T.A., Korsten L., Waals J.E.V.D. Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis causing blackleg on potatoes in South Africa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010;126:175–185. doi: 10.1007/s10658-009-9531-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022B02044-1/Research and application of potato germplasm resources innovation and breeding technology of detoxified seed potato in Xinjiang
- CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS/the Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sci-ences
- IVF2023/the Key Laboratory of Horticultural Crops Genetic Improvement, Ministry of Agriculture in China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

