Tribological Properties of Groove-Textured Ti-6Al-4V Alloys with Solid Lubricants in Dry Sliding against GCr15 Steel Balls
- PMID: 38004835
- PMCID: PMC10673546
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14111978
Tribological Properties of Groove-Textured Ti-6Al-4V Alloys with Solid Lubricants in Dry Sliding against GCr15 Steel Balls
Abstract
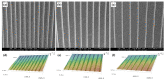
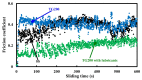
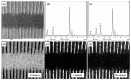
A nanosecond laser is used to fabricate groove-patterned textures on the upper surface of Ti-6Al-4V alloys, and then molybdic sulfide solid lubricants are filled into the grooves. The treated titanium alloy is subjected to friction and wear tests. The tribological performances of Ti-6Al-4V alloys are evaluated, and the wearing mechanism is analyzed. The combination of solid lubricants and surface texturing can effectively reduce the frictional coefficient and reduce the adhesion of Ti-6Al-4V materials on the steel balls for friction. The main wearing mechanism is the adhesive wear of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy and the adhesion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy materials on the surface of the steel balls. During the friction process, solid lubricants are squeezed from the grooves and coated at the friction interface to form a solid lubrication layer. This is the important reason why the combination of surface texturing and solid lubricants can improve the friction properties of titanium alloys effectively. The combination of solid lubricants and laser surface texturing provides an effective alternative way to improve the tribological properties of titanium alloy materials.
Keywords: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; friction; lubrication; textured groove.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Tribological behavior of Ti-6Al-4V against cortical bone in different biolubricants.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019 Feb;90:460-471. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 29. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019. PMID: 30448560
-
Study on improved tribological properties by alloying copper to CP-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Dec 1;57:123-32. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.046. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 26354247
-
Investigation on Wear Behavior of Cryogenically Treated Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy under Dry and Wet Conditions.Materials (Basel). 2019 Sep 4;12(18):2850. doi: 10.3390/ma12182850. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31487877 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of corrosion resistance between beta titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys: A systematic review.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126618. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126618. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663743
-
Femtosecond laser-induced surface nanostructures for tribological applications.In: König K, Ostendorf A, editors. Optically Induced Nanostructures: Biomedical and Technical Applications. Berlin: De Gruyter; 2015 Jun 23. Chapter 7. In: König K, Ostendorf A, editors. Optically Induced Nanostructures: Biomedical and Technical Applications. Berlin: De Gruyter; 2015 Jun 23. Chapter 7. PMID: 26491777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Luo H., Li J.-B., Ye J.-L., Tan J., Rashad M., Chen X.-H., Han S.-L., Zheng K.-H., Zhao T.-T., Pan F.-S. Effect of Ti-6Al-4V particle reinforcements on mechanical properties of Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 2022;32:3238–3249. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(22)66016-3. - DOI
-
- Zhang J.-H., Li X.-X., Xu D.-S., Yang R. Recent progress in the simulation of microstructure evolution in titanium alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. 2019;29:295–304. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2019.05.006. - DOI
-
- Dalmau A., Muñoz A.-I., Mischler S. Current and friction transients during tribocorrosion of a biomedical titanium alloy sliding against zirconia. Wear. 2023;524–525:204821. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2023.204821. - DOI
-
- Hua K., Zhang Y.-L., Zhang F., Kou H.-C., Li X.-L., Wu H.-X., Wang H.-F. Microstructure refinement and enhanced wear-resistance modulated by stress relaxation processing in a metastable β titanium alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021;181:111505. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111505. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

