Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids
- PMID: 38004886
- PMCID: PMC10673424
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14112029
Effects of the Electric Double Layer Characteristic and Electroosmotic Regulation on the Tribological Performance of Water-Based Cutting Fluids
Abstract
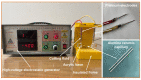
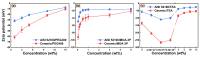
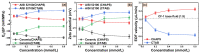
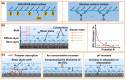
The electroosmosis effect is a complement to the theory of the traditional capillary penetration of cutting fluid. In this study, based on the electric double layer (EDL) characteristics at friction material/solution interfaces, the influences of additives and their concentrations on capillary electroosmosis were investigated, and a water-based cutting-fluid formulation with consideration to the electroosmosis effect was developed. The lubrication performance levels of cutting fluids were investigated by a four-ball tribometer. The results show that the EDL is compressed with increasing ionic concentration, which suppresses the electroosmotic flow (EOF). The specific adsorption of OH- ions or the dissociation of surface groups is promoted as pH rises, increasing the absolute zeta potential and EOF. The polyethylene glycol (PEG) additive adsorbed to the friction material surface can keep the shear plane away from the solid surface, reducing the absolute zeta potential and EOF. The electroosmotic performance of cutting fluid can be improved by compounding additives with different electroosmotic performance functions. Furthermore, electroosmotic regulators can adjust the zeta potential by the electrostatic adsorption mechanism, affecting the penetration performance of cutting fluid in the capillary zone at the friction interface. The improvement in the tribological performance of cutting fluid developed with consideration given to the electroosmosis effect is attributed to the enhancement of the penetration ability of the cutting fluid and the formation of more abundant amounts of lubricating film at the interface.
Keywords: electrical double layer; electroosmosis; tribological performance; water-based cutting fluid; zeta potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Electroosmotic flow: From microfluidics to nanofluidics.Electrophoresis. 2021 Apr;42(7-8):834-868. doi: 10.1002/elps.202000313. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Electrophoresis. 2021. PMID: 33382088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroosmotic flow velocity in DNA modified nanochannels.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Oct 1;553:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 3. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 31181468
-
Electroosmotic Flow Behavior of Viscoelastic LPTT Fluid in a Microchannel.Micromachines (Basel). 2019 Dec 15;10(12):881. doi: 10.3390/mi10120881. Micromachines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31847473 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacial Electric Effects on a Non-Isothermal Electroosmotic Flow in a Microcapillary Tube Filled by Two Immiscible Fluids.Micromachines (Basel). 2017 Jul 27;8(8):232. doi: 10.3390/mi8080232. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30400424 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of electroosmotic flow in capillary and microchip electrophoresis.J Chromatogr A. 2007 Nov 2;1170(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.08.083. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Chromatogr A. 2007. PMID: 17915240 Review.
References
-
- Yan P., Rong Y., Wang G. The Effect of Cutting Fluids Applied in Metal Cutting Process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016;230:19–37. doi: 10.1177/0954405415590993. - DOI
-
- Chen J., Liu D., Jin T., Qi Y. A Novel Bionic Micro-Textured Tool with the Function of Directional Cutting-Fluid Transport for Cutting Titanium Alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023;311:117816. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117816. - DOI
-
- Zhang K., Deng J., Xing Y., Li S., Gao H. Effect of Microscale Texture on Cutting Performance of WC/Co-Based TiAlN Coated Tools under Different Lubrication Conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015;326:107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.059. - DOI
-
- Diniz A.E., Micaroni R. Influence of the Direction and Flow Rate of the Cutting Fluid on Tool Life in Turning Process of AISI 1045 Steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007;47:247–254. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.04.003. - DOI
-
- Liu C.H., Sugihara T., Enomoto T. Interrupted Cutting of Inconel 718 with AlTiSiN Coated Cemented Carbide Tool under High Pressure Coolant Supply. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2022;78:124–133. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2022.07.012. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

