Nanoparticles and Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy for Cancer Treatment: Focus on Nanocarriers and a si-RNA CXCR4 Chemokine Blocker as Strategies for Tumor Eradication In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 38004925
- PMCID: PMC10673568
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14112068
Nanoparticles and Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy for Cancer Treatment: Focus on Nanocarriers and a si-RNA CXCR4 Chemokine Blocker as Strategies for Tumor Eradication In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
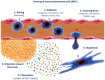
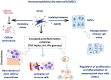
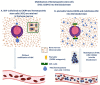
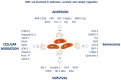
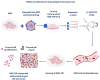
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have a high tropism for the hypoxic microenvironment of tumors. The combination of nanoparticles in MSCs decreases tumor growth in vitro as well as in rodent models of cancers in vivo. Covalent conjugation of nanoparticles with the surface of MSCs can significantly increase the drug load delivery in tumor sites. Nanoparticle-based anti-angiogenic systems (gold, silica and silicates, diamond, silver, and copper) prevented tumor growth in vitro. For example, glycolic acid polyconjugates enhance nanoparticle drug delivery and have been reported in human MSCs. Labeling with fluorescent particles (coumarin-6 dye) identified tumor cells using fluorescence emission in tissues; the conjugation of different types of nanoparticles in MSCs ensured success and feasibility by tracking the migration and its intratumor detection using non-invasive imaging techniques. However, the biosafety and efficacy; long-term stability of nanoparticles, and the capacity for drug release must be improved for clinical implementation. In fact, MSCs are vehicles for drug delivery with nanoparticles and also show low toxicity but inefficient accumulation in tumor sites by clearance of reticuloendothelial organs. To solve these problems, the internalization or conjugation of drug-loaded nanoparticles should be improved in MSCs. Finally, CXCR4 may prove to be a promising target for immunotherapy and cancer treatment since the delivery of siRNA to knock down this alpha chemokine receptor or CXCR4 antagonism has been shown to disrupt tumor-stromal interactions.
Keywords: CXCR4; PLAG; chemokine blockers (AMD-3100; exosomes; gene therapy; glycolic acid; homing; mesenchymal stem cells (MSC); nanocarriers; nanoparticles; plerixafor); stem cell therapy: CXCL12 (SDF-1 alpha); tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Imitola J., Raddassi K., Park K.I., Mueller F.J., Nieto M., Teng Y.D., Frenkel D., Li J., Sidman R.L., Walsh C.A., et al. Directed migration of neural stem cells to sites of CNS injury by the stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha/CXC chemokine receptor 4 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:18117–18122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408258102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

