Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS
- PMID: 38005205
- PMCID: PMC10672841
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227484
Zaluzanin C Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation in Kupffer Cells and Hepatocytes by Regulating Mitochondrial ROS
Abstract
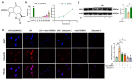
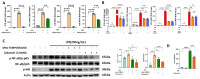
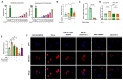
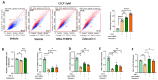
Zaluzanin C (ZC), a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Laurus nobilis L., has been reported to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, the mechanistic role of ZC in its protective effects in Kupffer cells and hepatocytes has not been elucidated. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the efficacy and mechanism of action of ZC in Kupffer cells and hepatocytes. ZC inhibited LPS-induced mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) production and subsequent mtROS-mediated NF-κB activity in Kupffer cells (KCs). ZC reduced mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Il1b and Tnfa) and chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl3, Ccl4, Cxcl2 and Cxcl9). Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced hepatocyte mtROS production was inhibited by ZC. ZC was effective in alleviating mtROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. ZC enhanced mitophagy and increased mRNA levels of fatty acid oxidation genes (Pparα, Cpt1, Acadm and Hadha) and mitochondrial biosynthetic factors (Pgc1α, Tfam, Nrf1 and Nrf2) in hepatocytes. ZC has proven its anti-lipid effect by improving lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by enhancing mitochondrial function to facilitate lipid metabolism. Therefore, our study suggests that ZC may be an effective compound for hepatoprotection by suppressing inflammation and lipid accumulation through regulating mtROS.
Keywords: NAFLD; Zaluzanin C; inflammation; lipid accumulation; mtROS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

