Assessing the Protective Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) against Water-Pipe Smoke-Induced Toxicity: A Comparative Study on Gene Expression and Histopathology
- PMID: 38005223
- PMCID: PMC10673035
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227502
Assessing the Protective Role of Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) against Water-Pipe Smoke-Induced Toxicity: A Comparative Study on Gene Expression and Histopathology
Abstract
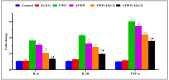
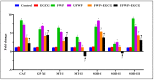
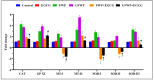
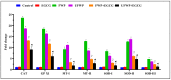
Exposure to water-pipe smoking, whether flavored or unflavored, has been shown to instigate inflammation and oxidative stress in BALB/c mice. This consequently results in alterations in the expression of inflammatory markers and antioxidant genes. This study aimed to scrutinize the impact of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)-a key active component of green tea-on inflammation and oxidative stress in BALB/c mice exposed to water-pipe smoke. The experimental setup included a control group, a flavored water-pipe smoke (FWP) group, an unflavored water-pipe smoke (UFWP) group, and EGCG-treated flavored and unflavored groups (FWP + EGCG and UFWP + EGCG). Expression levels of IL-6, IL1B, TNF-α, CAT, GPXI, MT-I, MT-II, SOD-I, SOD-II, and SOD-III were evaluated in lung, liver, and kidney tissues. Histopathological changes were also assessed. The findings revealed that the EGCG-treated groups manifested a significant decline in the expression of inflammatory markers and antioxidant genes compared to the FWP and UFWP groups. This insinuates that EGCG holds the capacity to alleviate the damaging effects of water-pipe smoke-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Moreover, enhancements in histopathological features were observed in the EGCG-treated groups, signifying a protective effect against tissue damage induced by water-pipe smoking. These results underscore the potential of EGCG as a protective agent against the adverse effects of water-pipe smoking. By curbing inflammation and oxidative stress, EGCG may aid in the prevention or mitigation of smoking-associated diseases.
Keywords: antioxidant genes; epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG); gene expression; histopathological examination; inflammatory markers; oxidative stress; water-pipe smoke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses cigarette smoke-induced inflammation in human cardiomyocytes via ROS-mediated MAPK and NF-κB pathways.Phytomedicine. 2019 May;58:152768. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.11.028. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31005721
-
Targeting HO-1 by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Contrast-Induced Renal Injury via Anti-Oxidative Stress and Anti-Inflammation Pathways.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 11;11(2):e0149032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149032. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26866373 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin -3- gallate mitigates diazinon neurotoxicity via suppression of pro-inflammatory genes and upregulation of antioxidant pathways.BMC Neurosci. 2025 Mar 10;26(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12868-025-00943-x. BMC Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40065246 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Green Tea Polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in Relation to Molecular Pathways Controlling Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 25;24(1):340. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010340. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate for Management of Heavy Metal-Induced Oxidative Stress: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Concerns.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4027. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084027. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dermaseptin B2 bioactive gene's potential for anticancer and anti-proliferative effect is linked to the regulation of the BAX/BBC3/AKT pathway.Med Oncol. 2024 May 20;41(6):162. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02384-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38767753
-
Cigarette Smoke Contributes to the Progression of MASLD: From the Molecular Mechanisms to Therapy.Cells. 2025 Feb 4;14(3):221. doi: 10.3390/cells14030221. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Against Iopromide-induced Injury in HEK-293 Cells via Anti-oxidative and Anti-inflammation Pathways.In Vivo. 2024 Nov-Dec;38(6):2617-2628. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13738. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 39477405 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanisms of EGCG in Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Liver Toxicity From Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 7;13(7):e70472. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70472. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40625629 Free PMC article.
-
Tamarix aphylla derived metabolites ameliorate indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats by modulating the MAPK signaling pathway, alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation: In vivo study supported by pharmacological network analysis.PLoS One. 2024 May 10;19(5):e0302015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302015. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38728332 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

