Resveratrol, ε-Viniferin, and Vitisin B from Vine: Comparison of Their In Vitro Antioxidant Activities and Study of Their Interactions
- PMID: 38005243
- PMCID: PMC10672907
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227521
Resveratrol, ε-Viniferin, and Vitisin B from Vine: Comparison of Their In Vitro Antioxidant Activities and Study of Their Interactions
Abstract
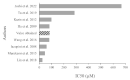
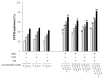
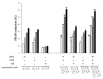
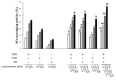
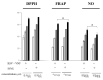
The control of oxidative stress with natural active substances could limit the development of numerous pathologies. Our objective was to study the antiradical effects of resveratrol (RSV), ε-viniferin (VNF), and vitisin B (VB) alone or in combination, and those of a standardized stilbene-enriched vine extract (SSVE). In the DPPH-, FRAP-, and NO-scavenging assays, RSV presented the highest activity with an IC50 of 81.92 ± 9.17, 13.36 ± 0.91, and 200.68 ± 15.40 µM, respectively. All binary combinations resulted in additive interactions in the DPPH- and NO-scavenging assays. In the FRAP assay, a synergic interaction for RSV + VNF, an additive for VNF + VB, and an antagonistic for RSV + VB were observed. The ternary combination of RSV + VNF + VB elicited an additive interaction in the DPPH assay and a synergic interaction in the FRAP- and NO-scavenging assays. There was no significant difference between the antioxidant activity of the SSVE and that of the combination of RSV + VNF. In conclusion, RSV presented the highest effects, followed by VNF and VB. The interactions revealed additive or synergistic effects, depending on the combination of the stilbenes and assay.
Keywords: antioxidant; interactions; resveratrol; stilbenes; vitisin B; ε-viniferin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Prior R., Wu X. Diet Antioxidant Capacity: Relationships to Oxidative Stress and Health. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013;5:126–139. doi: 10.5099/aj130200126. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

