Excellent Dark/Light Dual-Mode Photoresponsive Activities Based on g-C3N4/CMCh/PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogel Using Electron Beam Radiation Method
- PMID: 38005263
- PMCID: PMC10674341
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227544
Excellent Dark/Light Dual-Mode Photoresponsive Activities Based on g-C3N4/CMCh/PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogel Using Electron Beam Radiation Method
Abstract
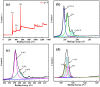
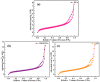
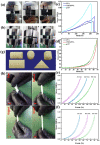
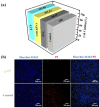
Photocatalytic technology for inactivating bacteria in water has received much attention. In this study, we reported a dark-light dual-mode sterilized g-C3N4/chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel (g-CP) prepared through freeze-thaw cycling and an in situ electron-beam radiation method. The structures and morphologies of g-CP were confirmed using Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction spectroscopy (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), solid ultraviolet diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET). Photocatalytic degradation experiments demonstrated that 1 wt% g-CP degraded rhodamine B (RhB) up to 65.92% in 60 min. At the same time, g-CP had good antimicrobial abilities for Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) within 4 h. The shapes of g-CP were adjustable (such as bar, cylinder, and cube) and had good mechanical properties and biocompatibility. The tensile and compressive modulus of 2 wt% g-CP were 0.093 MPa and 1.61 MPa, respectively. The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) test and Hoechst33342/PI double staining were used to prove that g-CP had good biocompatibility. It is expected to be applied to environmental sewage treatment and wound dressing in the future.
Keywords: cell activity; electron beam radiation method; g-CP hydrogel; photocatalytic antibacterial; photocatalytic degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Sudhaik A., Raizada P., Ahamad T., Alshehri S.M., Nguyen V., Le Q.V., Thakur S., Thakur V.K., Selvasembian R., Singh P. Recent advances in cellulose supported photocatalysis for pollutant mitigation: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022;226:1284–1308. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.241. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y.F., Xia Z., Yang Q., Wang L., Xing Y. Review on g-C3N4-based S-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022;125:128–144. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2022.02.035. - DOI
-
- Ren Y., Huang T., Zhao X., Wang K., Zhao L., Tao A., Jiang J., Yuan M., Wang J., Tu Q. Double network hydrogel based on curdlan and flaxseed gum with photothermal antibacterial properties for accelerating infectious wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;242:124715. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xie X.F., Lei H., Fan D. Antibacterial hydrogel with pH-responsive microcarriers of slow-release VEGF for bacterial infected wounds repair. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023;144:198–212. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2022.09.062. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2021GXYF021/the Key R&D Plan of Hubei Provincial Department of Science and Technology Hubei Provincial Colleges and Universities Outstanding Young and Middle-aged Technological Innovation Team Project Xianning City Key Program of Science & Technology
- No.T2020022/Hubei Provincial Colleges and Universities Outstanding Young and Middle-aged Technological Innovation Team Project
- No. 2021GXYF021/Xianning City Key Program of Science & Technology
- No.2020TD01, 2022FH09/the Science Development Foundation of Hubei University of Science & Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

