Study of the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of β-Carotene Based on Network Pharmacology
- PMID: 38005265
- PMCID: PMC10673508
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227540
Study of the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of β-Carotene Based on Network Pharmacology
Abstract
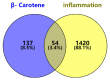
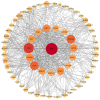
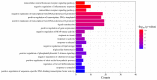
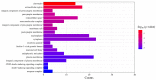
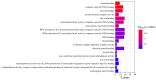
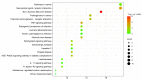
β-carotene is known to have pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-tumor properties. However, its main mechanism and related signaling pathways in the treatment of inflammation are still unclear. In this study, component target prediction was performed by using literature retrieval and the SwissTargetPrediction database. Disease targets were collected from various databases, including DisGeNET, OMIM, Drug Bank, and GeneCards. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed, and enrichment analysis of gene ontology and biological pathways was carried out for important targets. The analysis showed that there were 191 unique targets of β-carotene after removing repeat sites. A total of 2067 targets from the three databases were integrated, 58 duplicate targets were removed, and 2009 potential disease action targets were obtained. Biological function enrichment analysis revealed 284 biological process (BP) entries, 31 cellular component (CC) entries, 55 molecular function (MF) entries, and 84 cellular pathways. The biological processes were mostly associated with various pathways and their regulation, whereas the cell components were mainly membrane components. The main molecular functions included RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, DNA binding specific to the ligand activation sequence, DNA binding, steroid binding sequence-specific DNA binding, enzyme binding, and steroid hormone receptors. The pathways involved in the process included the TNF signaling pathway, sphingomyelin signaling pathway, and some disease pathways. Lastly, the anti-inflammatory signaling pathway of β-carotene was systematically analyzed using network pharmacology, while the molecular mechanism of β-carotene was further explored by molecular docking. In this study, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of β-carotene was preliminarily explored and predicted by bioinformatics methods, and further experiments will be designed to verify and confirm the predicted results, in order to finally reveal the anti-inflammatory mechanism of β-carotene.
Keywords: inflammatory; molecular docking; network pharmacology; β-carotene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

