Flavor Quality Analysis of Ten Actinidia arguta Fruits Based on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Headspace Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry
- PMID: 38005281
- PMCID: PMC10674867
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227559
Flavor Quality Analysis of Ten Actinidia arguta Fruits Based on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Headspace Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry
Abstract
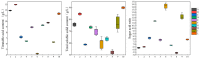
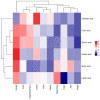
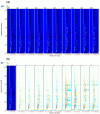
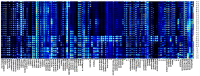
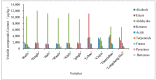
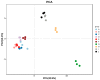
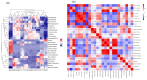
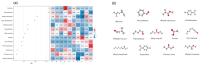
Actinidia arguta is a fruit crop with high nutritional and economic value. However, its flavor quality depends on various factors, such as variety, environment, and post-harvest handling. We analyzed the composition of total soluble sugars, titratable acids, organic acids, and flavor substances in the fruits of ten A. arguta varieties. The total soluble sugar content ranged from 4.22 g/L to 12.99 g/L, the titratable acid content ranged from 52.55 g/L to 89.9 g/L, and the sugar-acid ratio ranged from 5.39 to 14.17 at the soft ripe stage. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) showed that citric, quinic, and malic acids were the main organic acids in the A. arguta fruits. Headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) detected 81 volatile compounds in 10 A. arguta varieties, including 24 esters, 17 alcohols, 23 aldehydes, 7 ketones, 5 terpenes, 2 acids, 1 Pyrazine, 1 furan, and 1 benzene. Esters and aldehydes had the highest relative content of total volatile compounds. An orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) based on the odor activity value (OAV) revealed that myrcene, benzaldehyde, methyl isobutyrate, α-phellandrene, 3-methyl butanal, valeraldehyde, ethyl butyrate, acetoin, (E)-2-octenal, hexyl propanoate, terpinolene, 1-penten-3-one, and methyl butyrate were the main contributors to the differences in the aroma profiles of the fruits of different A. arguta varieties. Ten A. arguta varieties have different flavors. This study can clarify the differences between varieties and provide a reference for the evaluation of A. arguta fruit flavor, variety improvement and new variety selection.
Keywords: Actinidia arguta; HPLC; HS-GC-IMS; flavor; organic acids; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lai J.J., Li Z.Z., Man Y.P., Lei R., Wang Y.C. Genetic diversity of five wild Actinidia arguta populations native to China as revealed by SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2015;191:101–107. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.05.004. - DOI
-
- Zhang M., Wang H.X., Lou X., Zhao L.N., Yan D.L. Characterization of world Actinidia arguta variety resources and breeding trends. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017;36:3289–3297. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201711.041. - DOI
-
- Baranowska-Wojcik E., Szwajgier D. Characteristics and pro-health properties of mini kiwi (Actinidia arguta) Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2019;60:217–225. doi: 10.1007/s13580-018-0107-y. - DOI
-
- Wen J.L., Cao W.Y., Wang Y., He Y.L., Sun Y.N., Yuan P.Q., Sun B.W. Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of Actinidia arguta based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023:1–16. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2023020245. - DOI
-
- Hale I.L., Connolly B.A. Actinidia arguta: A new record of a naturalized introduction in connecticut. Rhodora. 2014;116:352–355. doi: 10.3119/14-01. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

