The Protective Effect of Marsdenia tenacissima against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Mediated by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis
- PMID: 38005304
- PMCID: PMC10674371
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227582
The Protective Effect of Marsdenia tenacissima against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Mediated by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis
Abstract
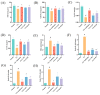
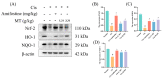
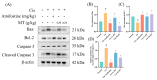
Cisplatin (Cis) is considered to be one of the most effective drugs for killing cancer cells and remains a first-line chemotherapeutic agent. However, Cis's multiple toxicities (especially nephrotoxicity) have limited its clinical use. Marsdenia tenacissima (Roxb.) Wight et Arn. (MT), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) employed extensively in China, not only enhances the antitumor effect in combination with Cis, but is also used for its detoxifying effect, as it reduces the toxic side effects of chemotherapy drugs. The aim of this study was to explore the therapeutic effect of MT on Cis-induced nephrotoxicity, along with its underlying mechanisms. In this study, liquid-mass spectrometry was performed to identify the complex composition of the extracts of MT. In addition, we measured the renal function, antioxidant enzymes, and inflammatory cytokines in mice with Cis-induced nephrotoxicity and conducted renal histology evaluations to assess renal injury. The expressions of the proteins related to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and apoptotic markers in renal tissues was detected by Western blotting (WB). MT treatment improved the renal function, decreased the mRNA expression of the inflammatory factors, and increased the antioxidant enzyme activity in mice. A better renal histology was observed after MT treatment. Further, MT inhibited the expression of the phospho-NFκB p65 protein/NFκB p65 protein (p-p65)/p65, phospho-inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase beta subunit/inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase beta subunit (p-IKKβ/IKKβ), Bcl-2-associated X (Bax), and Cleaved Caspase 3/Caspase 3 proteins, while the expression of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), Recombinant NADH Dehydrogenase, Quinone 1 (NQO1), and B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) was increased. The present study showed that MT ameliorated renal injury, which mainly occurs through the regulation of the Nrf2 pathway, the NF-κB pathway, and the suppression of renal tissue apoptosis. It also suggests that MT can be used as an adjuvant to mitigate the nephrotoxicity of Cis chemotherapy.
Keywords: Marsdenia tenacissima; apoptosis; cisplatin; inflammation; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that would appear to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sinapic acid modulates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:646-653. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.085. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28686978
-
S-Allylmercaptocysteine Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity through Suppression of Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation.Nutrients. 2017 Feb 20;9(2):166. doi: 10.3390/nu9020166. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28230744 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the protection of growth hormone in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: The impact of IGF-1 on the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 signaling.Life Sci. 2020 Jul 15;253:117581. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117581. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32209424
-
Ergothioneine mitigates cisplatin-evoked nephrotoxicity via targeting Nrf2, NF-κB, and apoptotic signaling and inhibiting γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.Life Sci. 2021 Aug 1;278:119572. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119572. Epub 2021 May 6. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33964294
-
Piracetam mitigates nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin via the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt and MAPK/JNK/ERK signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112511. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112511. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38909496
Cited by
-
Biomarker Discovery and Molecular Docking Reveal Marsdenia tenacissima Fermentation Product's Anti-Lung Cancer Components.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 6;47(6):427. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060427. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699827 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

