Effects of Harvest Time and Hydrodistillation Time on Yield, Composition, and Antioxidant Activity of Mint Essential Oil
- PMID: 38005307
- PMCID: PMC10675317
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227583
Effects of Harvest Time and Hydrodistillation Time on Yield, Composition, and Antioxidant Activity of Mint Essential Oil
Abstract
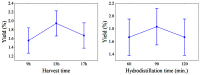
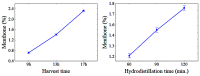
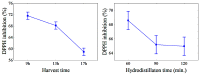
In this study, we assessed the effects of different harvest times (9 a.m., 1 p.m., and 5 p.m.) and hydrodistillation times (60, 90, and 120 min) on the yield, chemical composition, and antioxidant activity of the spearmint (Mentha spicata L.) essential oil (EO) sourced from the Amazon region. EO yield was ≥1.55% and was not significantly influenced (p ≥ 0.05) by the different harvest times and hydrodistillation times. Thirty-one different organic compounds were identified, of which menthol (91.56-95.68%), menthone (0.6-2.72%), and isomenthone (0.55-1.46%) were the major constituents. The highest menthol content in the EO was obtained from samples collected at 9 a.m., with a hydrodistillation time of 60-90 min, compared to other harvest and hydrodistillation times. This suggests that exposure to sun and light, which is greater at harvest times of 1 p.m. and 5 p.m., decreased the menthol content and altered the chemical composition of Mentha EO. Furthermore, the sample harvested at 9 a.m. and hydrodistilled for 60 min showed the highest antioxidant activity (61.67 equivalent mg of Trolox per g of EO), indicating that antioxidant activity is strongly affected by light exposure and the contact duration of the sample with boiling water during hydrodistillation.
Keywords: Mentha spicata L.; diurnal variation; gas chromatography; menthol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mokhtarikhah G., Ebadi M.-T., Ayyari M. Qualitative Changes of Spearmint Essential Oil as Affected by Drying Methods. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020;153:112492. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112492. - DOI
-
- Brahmi F., Khodir M., Mohamed C., Pierre D. Chemical composition and biological activities of Mentha species. In: El-Shemy H., editor. Aromatic and Medicinal Plants-Back to Nature. 1st ed. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2017. pp. 47–79. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

