Putative Identification of New Phragmaline-Type Limonoids from the Leaves of Swietenia macrophylla King: A Case Study Using Mass Spectrometry-Based Molecular Networking
- PMID: 38005325
- PMCID: PMC10673509
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227603
Putative Identification of New Phragmaline-Type Limonoids from the Leaves of Swietenia macrophylla King: A Case Study Using Mass Spectrometry-Based Molecular Networking
Abstract
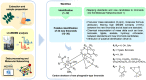
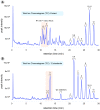
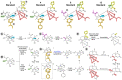
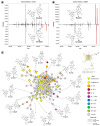
Swietenia macrophylla King is a plant commonly known as Brazilian mahogany. The wood from its stem is highly prized for its exceptional quality, while its leaves are valued for their high content of phragmalin-type limonoids, a subclass of compounds known for their significant biological activities, including antimalarial, antitumor, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties. In this context, twelve isolated limonoids from S. macrophylla leaves were employed as standards in mass spectrometry-based molecular networking to unveil new potential mass spectrometry signatures for phragmalin-type limonoids. Consequently, ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry was utilized for data acquisition. Subsequently, the obtained data were analyzed using the Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking platform based on spectral similarity. In summary, this study identified 24 new putative phragmalin-type limonoids for the first time in S. macrophylla. These compounds may prove valuable in guiding future drug development efforts, leveraging the already established biological activities associated with limonoids.
Keywords: GNPS; Meliaceae; limonoids; mahogany; mass spectrometry; molecular networking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Swieteliacates S-U, phragmalin limonoids, from the leaves of Swietenia macrophylla.Org Biomol Chem. 2024 Mar 13;22(11):2182-2186. doi: 10.1039/d3ob02113k. Org Biomol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38390690
-
Limonoids of the phragmalin type from Swietenia macrophylla and their chemotaxonomic significance.J Nat Prod. 2008 Dec;71(12):1983-7. doi: 10.1021/np800312h. J Nat Prod. 2008. PMID: 19053509
-
Mexicanolide-type limonoids from the seeds of Swietenia macrophylla.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2018 Apr;20(4):299-305. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2017.1335715. Epub 2017 Jun 1. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2018. PMID: 28569087
-
Chemical Structures and Biological Activities of Limonoids from the Genus Swietenia (Meliaceae).Molecules. 2018 Jun 29;23(7):1588. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071588. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29966275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
13C NMR spectroscopy of D and B, D-ring seco-limonoids of Meliaceae family.Nat Prod Res. 2008 Jun 15;22(9):763-800. doi: 10.1080/14786410701628812. Nat Prod Res. 2008. PMID: 18569718 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicity and Metabolomic Dysfunction Invoked by Febrifugin, a Harmful Component of Edible Nut of Swietenia macrophylla.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 9;25(17):9753. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179753. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flores T.B. Meliaceae in Flora Do Brasil 2020 Em Construção. [(accessed on 30 December 2020)]; Available online: http://reflora.jbrj.gov.br/reflora/floradobrasil/FB23803.
-
- Grogan J., Barreto P., Veríssimo A. Mogno Na Amazônia Brasileira: Ecologia E Perspectivas de Manejo. Imazon; Belém, Brazil: 2002.
-
- Eid A.M.M., Elmarzugi N.A., El-Enshasy H.A. A Review on the Phytopharmacological Effect of Swietenia Macrophylla. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013;5:47–53.
-
- Champagne D.E., Koul O., Isman M.B., Scudder G.G.E., Neil Towers G.H. Biological Activity of Limonoids from the Rutales. Phytochemistry. 1992;31:377–394. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(92)90003-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

