Research Progress on Natural Plant Molecules in Regulating the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38005352
- PMCID: PMC10674591
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227631
Research Progress on Natural Plant Molecules in Regulating the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder. With the aging population and the continuous development of risk factors associated with AD, it will impose a significant burden on individuals, families, and society. Currently, commonly used therapeutic drugs such as Cholinesterase inhibitors, N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists, and multiple AD pathology removal drugs have been shown to have beneficial effects on certain pathological conditions of AD. However, their clinical efficacy is minimal and they are associated with certain adverse reactions. Furthermore, the underlying pathological mechanism of AD remains unclear, posing a challenge for drug development. In contrast, natural plant molecules, widely available, offer multiple targeting pathways and demonstrate inherent advantages in modifying the typical pathologic features of AD by influencing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). We provide a comprehensive review of recent in vivo and in vitro studies on natural plant molecules that impact the BBB in the treatment of AD. Additionally, we analyze their specific mechanisms to offer novel insights for the development of safe and effective targeted drugs as well as guidance for experimental research and the clinical application of drugs for the prevention and treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood–brain barrier; mechanisms; natural plant molecules; research progress; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
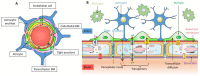




References
-
- 2023 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. [(accessed on 6 November 2023)];Alzheimers Dement. 2023 19:1598–1695. doi: 10.1002/alz.13016. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rj.... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang R.T., Liu Y. Epidemiological research progress on Alzheimer’s disease. Chin. J. Prev. Control. Chronic No-Commun. Dis. 2021;29:707–711.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

