Identification of Sanguinarine Metabolites in Rats Using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS
- PMID: 38005364
- PMCID: PMC10674372
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28227641
Identification of Sanguinarine Metabolites in Rats Using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS
Abstract
Sanguinarine (SAN), as the main active component of a traditional Chinese veterinary medicine, has been widely used in the animal husbandry and breeding industry. However, the metabolites of SA are still uncertain. Therefore, this research aimed to investigate the metabolites of SA based on rats in vivo. The blood, feces, and urine of rats were collected after the oral administration of 40 mg/kg SAN. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) was employed to identify the metabolites of SAN. The elemental composition of sanguinarine metabolites was inferred by analyzing their exact molecular weight, and the structures of the metabolites were predicted based on their fragment ions and cleavage pathways. A total of 12 metabolites were identified, including three metabolites in the plasma, four in the urine, and nine in the feces. According to the possible metabolic pathways deduced in this study, SAN was mainly metabolized through reduction, oxidation, demethylation, hydroxylation, and glucuronidation. This present research has summarized the metabolism of SAN in rats, which is helpful for further studying the metabolic mechanism of SAN in vivo and in vitro.
Keywords: UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS; in vivo; metabolites; rats; sanguinarine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
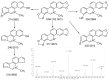
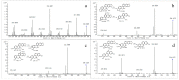


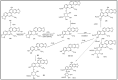
References
-
- Danielewski M., Zielińska S., Matuszewska A., Słupski W., Włodarczyk M., Jęśkowiak I., Wiatrak B., Kowalski K., Jezierska-Domaradzka A., Ziółkowski P., et al. Sanguinarine-Chelerythrine Fraction of Coptis Chinensis Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Carrageenan Paw Oedema Test in Rats and Reveals Reduced Gastrotoxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022;2022:1504929. doi: 10.1155/2022/1504929. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao L., Alvensleben S.V., Fusconi G., Morlacchini M. Safety Evaluation of a Standardized Macleaya Cordata Extract in a Ninety Day Feeding Study in Weaned Piglets. Open J. Anim. Sci. 2017;7:213–231. doi: 10.4236/ojas.2017.72017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

