A Novel, Efficient Algorithm for Subsurface Radar Imaging below a Non-Planar Surface
- PMID: 38005409
- PMCID: PMC10675197
- DOI: 10.3390/s23229021
A Novel, Efficient Algorithm for Subsurface Radar Imaging below a Non-Planar Surface
Abstract
In classical radar imaging, such as in Earth remote sensing, electromagnetic waves are usually assumed to propagate in free space. However, in numerous applications, such as ground penetrating radar or non-destructive testing, this assumption no longer holds. When there is a multi-material background, the subsurface image reconstruction becomes considerably more complex. Imaging can be performed in the spatial domain or, equivalently, in the wavenumber domain (k-space). In subsurface imaging, to date, objects with a non-planar surface are commonly reconstructed in the spatial domain, by the Backprojection algorithm combined with ray tracing, which is computationally demanding. On the other hand, objects with a planar surface can be reconstructed more efficiently in k-space. However, many non-planar surfaces are partly planar. Therefore, in this paper, a novel concept is introduced that makes use of the efficient k-space-based reconstruction algorithms for partly planar scenarios, too. The proposed algorithm forms an image from superposing sub-images where as many image parts as possible are reconstructed in the wavenumber domain, and only as many as necessary are reconstructed in the spatial domain. For this, a segmentation scheme is developed to determine which parts of the image volume can be reconstructed in the wavenumber domain. The novel concept is verified by measurements, both from monostatic synthetic aperture radar data and multiple-input-multiple-output radar data. It is shown that the computational efficiency for imaging irregularly shaped geometries can be significantly augmented when applying the proposed concept.
Keywords: MIMO radar; ground penetrating radar; non-destructive testing; radar; subsurface imaging; synthetic aperture radar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

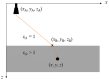


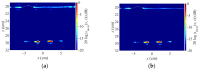
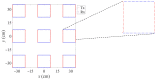

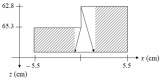

References
-
- Cumming I.G., Wong F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. Artech House; Boston, MA, USA: 2005. SAR Processing Algorithms; pp. 223–362.
-
- Soumekh M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms. John Wiley and Sons; New York, NY, USA: 1999.
-
- Ahmed S.S., Schiessl A., Gumbmann F., Tiebout M., Methfessel S., Schmidt L.-P. Advanced microwave imaging. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2012;13:26–43. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2012.2205772. - DOI
-
- Ahmed S.S. Microwave Imaging in Security—Two Decades of Innovation. IEEE J. Microw. 2021;1:191–201. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2020.3035790. - DOI
-
- Laribi A., Hahn M., Dickmann J., Waldschmidt C. Performance Investigation of Automotive SAR Imaging; Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM); Munich, Germany. 15–17 April 2018; pp. 1–4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

