Non-Invasive Glucose Sensing Technologies and Products: A Comprehensive Review for Researchers and Clinicians
- PMID: 38005523
- PMCID: PMC10674292
- DOI: 10.3390/s23229130
Non-Invasive Glucose Sensing Technologies and Products: A Comprehensive Review for Researchers and Clinicians
Abstract
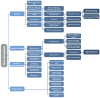
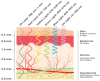
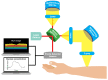
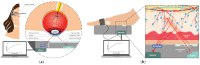
Diabetes Mellitus incidence and its negative outcomes have dramatically increased worldwide and are expected to further increase in the future due to a combination of environmental and social factors. Several methods of measuring glucose concentration in various body compartments have been described in the literature over the years. Continuous advances in technology open the road to novel measuring methods and innovative measurement sites. The aim of this comprehensive review is to report all the methods and products for non-invasive glucose measurement described in the literature over the past five years that have been tested on both human subjects/samples and tissue models. A literature review was performed in the MDPI database, with 243 articles reviewed and 124 included in a narrative summary. Different comparisons of techniques focused on the mechanism of action, measurement site, and machine learning application, outlining the main advantages and disadvantages described/expected so far. This review represents a comprehensive guide for clinicians and industrial designers to sum the most recent results in non-invasive glucose sensing techniques' research and production to aid the progress in this promising field.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus; continuous; glucose sensing; intermittent; non-invasive; product design and development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

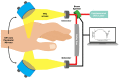
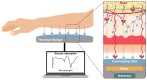
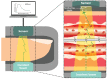
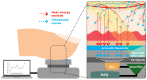




References
-
- WHO Diabetes. 2023. [(accessed on 1 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes.
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare . Diabetes: Australian Facts. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; Canberra, Australia: 2023.
-
- WHO The Top 10 Causes of Death. 2020. [(accessed on 1 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

