Bridge Model Updating Based on Wavelet Neural Network and Wind-Driven Optimization
- PMID: 38005571
- PMCID: PMC10674818
- DOI: 10.3390/s23229185
Bridge Model Updating Based on Wavelet Neural Network and Wind-Driven Optimization
Abstract
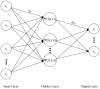
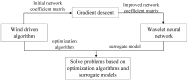
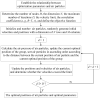
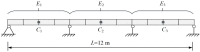
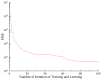
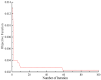
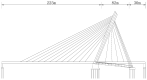
Aging, corrosive environments, and inadequate maintenance may result in performance deterioration of civil infrastructures, and finite element model updating is a commonly employed structural health monitoring procedure in civil engineering to reflect the current situation and to ensure the safety and serviceability of structures. Using the finite element model updating process to obtain the relationship between the structural responses and updating parameters, this paper proposes a method of using the wavelet neural network (WNN) as the surrogate model combined with the wind-driven optimization (WDO) algorithm to update the structural finite element model. The method was applied to finite element model updating of a continuous beam structure of three equal spans to verify its feasibility, the results show that the WNN can reflect the nonlinear relationship between structural responses and the parameters and has an outstanding simulation performance; the WDO has an excellent ability for optimization and can effectively improve the efficiency of model updating. Finally, the method was applied to update a real bridge model, and the results show that the finite element model update based on WDO and WNN is applicable to the updating of a multi-parameter bridge model, which has practical significance in engineering and high efficiency in finite element model updating. The differences between the updated values and measured values are all within the range of 5%, while the maximum difference was reduced from -10.9% to -3.6%. The proposed finite element model updating method is applicable and practical for multi-parameter bridge model updating and has the advantages of high updating efficiency, reliability, and practical significance.
Keywords: bridge; finite element model updating; surrogate model; wavelet neural network; wind-driven optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
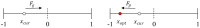

Similar articles
-
Research on Multi-Alternatives Problem of Finite Element Model Updating Based on IAFSA and Kriging Model.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;20(15):4274. doi: 10.3390/s20154274. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751863 Free PMC article.
-
Finite Element Model Updating of RC Bridge Structure with Static Load Testing: A Case Study of Vietnamese ThiThac Bridge in Coastal and Marine Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;22(22):8884. doi: 10.3390/s22228884. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433489 Free PMC article.
-
Modal test and finite element updating of sprayer boom truss.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):22860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73640-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39354090 Free PMC article.
-
Structural damage detection using finite element model updating with evolutionary algorithms: a survey.Neural Comput Appl. 2018;30(2):389-411. doi: 10.1007/s00521-017-3284-1. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Neural Comput Appl. 2018. PMID: 29950788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Machine Learning Approach as a Surrogate for a Finite Element Analysis: Status of Research and Application to One Dimensional Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 27;21(5):1654. doi: 10.3390/s21051654. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;25(15):4831. doi: 10.3390/s25154831. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40807997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chrysanidis T. Experimental and numerical research on cracking characteristics of medium-reinforced prisms under variable uniaxial degrees of elongation. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023;145:107014. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.107014. - DOI
-
- Chrysanidis T.A., Panoskaltsis V.P. Experimental investigation on cracking behavior of reinforced concrete tension ties. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022;16:e00810. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00810. - DOI
-
- Chrysanidis T., Mousama D., Tzatzo E., Alamanis N., Zachos D. Study of the Effect of a Seismic Zone to the Construction Cost of a Five-Story Reinforced Concrete Building. Sustainability. 2022;14:10076. doi: 10.3390/su141610076. - DOI
-
- Gong C., Wang Y., Peng Y., Ding W., Lei M., Da Z., Shi C. Three-dimensional coupled hydromechanical analysis of localized joint leakage in segmental tunnel linings. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022;130:104726. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2022.104726. - DOI
-
- Razavi M., Hadidi A. Structural damage identification through sensitivity-based finite element model updating and wavelet packet transform component energy. Structures. 2021;33:4857–4870. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.07.030. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

