Stereoselective Voltammetric Biosensor for Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro-Inositol Recognition
- PMID: 38005597
- PMCID: PMC10674735
- DOI: 10.3390/s23229211
Stereoselective Voltammetric Biosensor for Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro-Inositol Recognition
Abstract
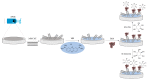
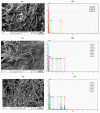
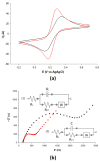
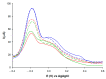
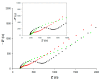
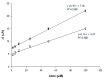
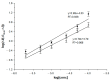
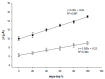
This paper describes the development of a simple voltammetric biosensor for the stereoselective discrimination of myo-inositol (myo-Ins) and D-chiro-inositol (D-chiro-Ins) by means of bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorption onto a multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) graphite screen-printed electrode (MWCNT-GSPE), previously functionalized by the electropolymerization of methylene blue (MB). After a morphological characterization, the enantioselective biosensor platform was electrochemically characterized after each modification step by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The results show that the binding affinity between myo-Ins and BSA was higher than that between D-chiro-Ins and BSA, confirming the different interactions exhibited by the novel BSA/MB/MWCNT/GSPE platform towards the two diastereoisomers. The biosensor showed a linear response towards both stereoisomers in the range of 2-100 μM, with LODs of 0.5 and 1 μM for myo-Ins and D-chiro-Ins, respectively. Moreover, a stereoselectivity coefficient α of 1.6 was found, with association constants of 0.90 and 0.79, for the two stereoisomers, respectively. Lastly, the proposed biosensor allowed for the determination of the stereoisomeric composition of myo-/D-chiro-Ins mixtures in commercial pharmaceutical preparations, and thus, it is expected to be successfully applied in the chiral analysis of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs of forensic interest.
Keywords: D-chiro-inositol; MWCNTs; biosensor; myo-inositol; stereoselective recognition; voltammetric detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Unfer V., Dewailly D. A Clinical Guide to Inositols. Elsevier Academic Press; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2023.
-
- Facchinetti F., Dante G., Neri I. Frontiers in Gynecological Endocrinology. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. The ratio of MI to DCI and its impact in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: Experimental and literature evidences; pp. 103–109.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

