Artifact Augmentation for Enhanced Tissue Detection in Microscope Scanner Systems
- PMID: 38005629
- PMCID: PMC10675542
- DOI: 10.3390/s23229243
Artifact Augmentation for Enhanced Tissue Detection in Microscope Scanner Systems
Abstract
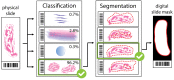
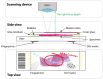
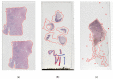
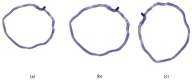
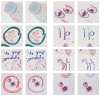
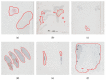
As the field of routine pathology transitions into the digital realm, there is a surging demand for the full automation of microscope scanners, aiming to expedite the process of digitizing tissue samples, and consequently, enhancing the efficiency of case diagnoses. The key to achieving seamless automatic imaging lies in the precise detection and segmentation of tissue sample regions on the glass slides. State-of-the-art approaches for this task lean heavily on deep learning techniques, particularly U-Net convolutional neural networks. However, since samples can be highly diverse and prepared in various ways, it is almost impossible to be fully prepared for and cover every scenario with training data. We propose a data augmentation step that allows artificially modifying the training data by extending some artifact features of the available data to the rest of the dataset. This procedure can be used to generate images that can be considered synthetic. These artifacts could include felt pen markings, speckles of dirt, residual bubbles in covering glue, or stains. The proposed approach achieved a 1-6% improvement for these samples according to the F1 Score metric.
Keywords: U-Net; augmentation; classification; convolutional neural network; deep learning; digital microscope scanner; digital pathology; segmentation; tissue detection.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors D.K., L.K., Á.S., R.P., V.J. and B.M. were employed by the company 3DHISTECH Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from 3DHISTECH Ltd. The funder had the following involvement with the study: financing research costs, data collection and result validation.
Figures





References
-
- Farahani N., Parwani A.V., Pantanowitz L. Whole slide imaging in pathology: Advantages, limitations, and emerging perspectives. Pathol. Lab. Med. Int. 2015;7:23–33. doi: 10.2147/PLMI.S59826. - DOI
-
- Patel A., Balis U.G., Cheng J., Li Z., Lujan G., McClintock D.S., Pantanowitz L., Parwani A. Contemporary Whole Slide Imaging Devices and Their Applications within the Modern Pathology Department: A Selected Hardware Review. J. Pathol. Inform. 2021;12:50. doi: 10.4103/jpi.jpi_66_21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

