Foliar Application of Sulfur-Containing Compounds-Pros and Cons
- PMID: 38005690
- PMCID: PMC10674314
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223794
Foliar Application of Sulfur-Containing Compounds-Pros and Cons
Abstract
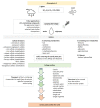
Sulfate is taken up from the soil solution by the root system; and inside the plant, it is assimilated to hydrogen sulfide, which in turn is converted to cysteine. Sulfate is also taken up by the leaves, when foliage is sprayed with solutions containing sulfate fertilizers. Moreover, several other sulfur (S)-containing compounds are provided through foliar application, including the S metabolites hydrogen sulfide, glutathione, cysteine, methionine, S-methylmethionine, and lipoic acid. However, S compounds that are not metabolites, such as thiourea and lignosulfonates, along with dimethyl sulfoxide and S-containing adjuvants, are provided by foliar application-these are the S-containing agrochemicals. In this review, we elaborate on the fate of these compounds after spraying foliage and on the rationale and the efficiency of such foliar applications. The foliar application of S-compounds in various combinations is an emerging area of agricultural usefulness. In the agricultural practice, the S-containing compounds are not applied alone in spray solutions and the need for proper combinations is of prime importance.
Keywords: foliar fertilization; foliar spraying; sulfur-containing adjuvants; sulfur-containing agrochemicals; sulfur-containing metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fernández V., Sotiropoulos T., Brown P. Foliar Fertilization: Scientific Principles and Field Practices. 1st ed. International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA); Paris, France: 2013.
-
- Fageria N.K., Barbosa Filho M.P., Moreira A., Guimarães C.M. Foliar Fertilization of Crop Plants. J. Plant Nutr. 2009;32:1044–1064. doi: 10.1080/01904160902872826. - DOI
-
- Niu J., Liu C., Huang K., Liu M., Yan D. Effects of Foliar Fertilization: A Review of Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021;21:104–118. doi: 10.1007/s42729-020-00346-3. - DOI
-
- Ishfaq M., Kiran A., ur Rehman H., Farooq M., Ijaz N.H., Nadeem F., Azeem I., Li X., Wakeel A. Foliar nutrition: Potential and challenges under multifaceted agriculture. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022;200:104909. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104909. - DOI
-
- Alshaal T., El-Ramady H. Foliar Application: From Plant Nutrition to Biofortification. Environ. Biodivers. Soil Secur. 2017;1:71–83. doi: 10.21608/jenvbs.2017.1089.1006. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

