Current Status of Biotechnological Approaches to Enhance the Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in India-A Review
- PMID: 38005713
- PMCID: PMC10675783
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223816
Current Status of Biotechnological Approaches to Enhance the Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in India-A Review
Abstract
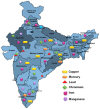
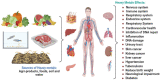
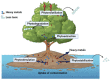
Rising waste construction, agricultural actions, and manufacturing sewages all contribute to heavy metal accumulation in water resources. Humans consume heavy metals-contaminated substances to make sustenance, which equally ends up in the food circle. Cleaning of these vital properties, along with the prevention of new pollution, has long been required to evade negative strength consequences. Most wastewater treatment techniques are widely acknowledged to be costly and out of the grasp of governments and small pollution mitigation businesses. Utilizing hyper-accumulator plants that are extremely resilient to heavy metals in the environment/soil, phytoremediation is a practical and promising method for eliminating heavy metals from contaminated environments. This method extracts, degrades, or detoxifies harmful metals using green plants. The three phytoremediation techniques of phytostabilization, phytoextraction, and phytovolatilization have been used extensively for soil remediation. Regarding their ability to be used on a wide scale, conventional phytoremediation methods have significant limitations. Hence, biotechnological attempts to change plants for heavy metal phytoremediation methods are extensively investigated in order to increase plant effectiveness and possible use of improved phytoremediation approaches in the country of India. This review focuses on the advances and significance of phytoremediation accompanied by the removal of various harmful heavy metal contaminants. Similarly, sources, heavy metals status in India, impacts on nature and human health, and variables influencing the phytoremediation of heavy metals have all been covered.
Keywords: accumulation; detection; food chain; heavy metals; phytoremediation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: An eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach.Chemosphere. 2022 Sep;303(Pt 1):134788. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134788. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35504464 Review.
-
Clean-Up of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Soil by Phytoremediation: A Multidisciplinary and Eco-Friendly Approach.Toxics. 2023 May 2;11(5):422. doi: 10.3390/toxics11050422. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37235237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omics approaches in effective selection and generation of potential plants for phytoremediation of heavy metal from contaminated resources.J Environ Manage. 2023 Jun 15;336:117730. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117730. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Environ Manage. 2023. PMID: 36921476 Review.
-
Phytoremediation technologies and their mechanism for removal of heavy metal from contaminated soil: An approach for a sustainable environment.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 27;14:1076876. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1076876. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36778693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical review on the phytoremediation of heavy metals from environment: Performance and challenges.Chemosphere. 2022 Mar;291(Pt 3):132979. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132979. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34801572 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of bacterial γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase increases toxic metal(loid)s tolerance and accumulation in Crambe abyssinica.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Oct 23;43(11):270. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03351-3. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443376 Free PMC article.
-
Phytoremediation Potential of Different Genotypes of Salix alba and S. viminalis.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;13(5):735. doi: 10.3390/plants13050735. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dhingra N., Sharma R., Singh N.S. Phytoremediation for Environmental Sustainability. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2022. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil and Water; pp. 47–70.
-
- Bijekar S., Padariya H.D., Yadav V.K., Gacem A., Hasan M.A., Awwad N.S., Yadav K.K., Islam S., Park S., Jeon B.-H. The state of the art and emerging trends in the wastewater treatment in developing nations. Water. 2022;14:2537. doi: 10.3390/w14162537. - DOI
-
- Singh B.R., Steinnes E. Soil Processes and Water Quality. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2020. Soil and water contamination by heavy metals; pp. 233–271.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources