Application of Bacillus spp. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Improves Common Bean Production Compared to Conventional Fertilization
- PMID: 38005724
- PMCID: PMC10675661
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223827
Application of Bacillus spp. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Improves Common Bean Production Compared to Conventional Fertilization
Abstract
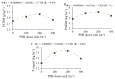
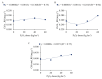
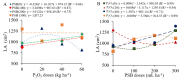
The use of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) can be a sustainable strategy to increase phosphorus availability and promote satisfactory crop yields. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether inoculation with PSB in common bean increases (i) growth, (ii) nutrition, (iii) yield, and (iv) grain quality, and (v) reduces the chemical phosphorus application dose to obtain maximum yields. The experiment was conducted in an Oxisol using a randomized block design in a 4 × 4 factorial scheme, with four replicates, using the cultivar IAC 2051. The first factor was four doses of P2O5 (0, 20, 40 and 60 kg ha-1), and the second factor was four doses of PSB (0, 100, 200 and 300 mL ha-1). For leaf area and leaf chlorophyll content, the association of PSB inoculation with a P2O5 dose of 40 kg ha-1 promoted the best conditions for the common bean. P2O5 application increased yield by 79 kg ha-1 for each 10 kg ha-1 added. PSB inoculation at a dose of 192 mL ha-1 promoted P export of 15.3 kg ha-1, and the PSB dose of 159 mL ha-1 increased yield by 389 kg ha-1 (12%) compared to the control. Grain quality remained within the standards required by the consumer market, being little affected by the treatments. Improvements in common bean growth and nutritional and physiological status promoted by P2O5 application and PSB were essential in increasing yield, so these are sustainable production strategies.
Keywords: Bacillus megaterium; Bacillus subtilis; Phaseolus vulgaris L.; phosphorus; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Almeida C.P., Paulino J.F.C., Carbonell S.A.M., Chiorato A.F., Song Q., Vittori V.D., Rodriguez M., Papa R., Benchimol-Reis L.L. Genetic diversity, population structure, and andean introgression in Brazilian common bean cultivars after half a century of genetic breeding. Genes. 2020;11:1298. doi: 10.3390/genes11111298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vougeleka V., Savvas D., Ntatsi G., Ellinas G., Zacharis A., Iannetta P.P.M., Mylona P., Saitanis C.J. Impact of the rootstock genotype on the performance of grafted common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2023;311:111821. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111821. - DOI
-
- Hungria M., Vargas M.A. Environmental factors affecting N2 fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crops Res. 2000;65:151–164. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00084-2. - DOI
-
- Barros R.L.N., Oliveira L.B., Magalhães W.B., Médici L.O., Pimentel C. Interaction of biological nitrogen fixation with sowing nitrogen fertilization on common bean in the two seasons of cultivation in Brazil. J. Plant Nutr. 2018;41:774–781. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2018.1426016. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

