Therapeutics to Treat Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders: A Promising Perspective from Algerian Traditional Medicine
- PMID: 38005756
- PMCID: PMC10674704
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223860
Therapeutics to Treat Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders: A Promising Perspective from Algerian Traditional Medicine
Abstract
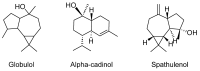
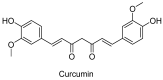
Ancient people sought out drugs in nature to prevent, cure, and treat their diseases, including mental illnesses. Plants were their primary source for meeting their healthcare needs. In Algeria, folk medicine remains a fundamental part of the local intangible knowledge. This study aims to conduct a comprehensive ethnomedicinal investigation and documentation of medicinal plants and the different plant formulations traditionally used in Algeria for the treatment of pain, psychiatric, and neurological disorders. It also intends to improve the current knowledge of Algerian folk medicine. Several scientific databases were used to accomplish this work. Based on this investigation, we identified 82 plant species belonging to 69 genera and spanning 38 distinct botanical families used as remedies to treat various psychological and neurological conditions. Their traditional uses and methods of preparation, along with their phytochemical composition, main bioactive constituents, and toxicity were noted. Therefore, this review provides a new resource of information on Algerian medicinal plants used in the treatment and management of neurological and psychological diseases, which can be useful not only for the documentation and conservation of traditional knowledge, but also for conducting future phytochemical and pharmacological studies.
Keywords: Africa; Algeria; Ayurveda; CNS; Chinese medicine; ethnobotanical; medicinal plants; neurological disorders; pharmacopoeia; psychiatric; traditional healers; traditional medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












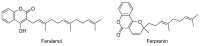
References
-
- Quezel P., Santa S. New Flora of Algeria and Southern Desert Regions. Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique; Paris, France: 1962.
-
- Ozenda P. Flore du Sahara Septentrional et Central. Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique; Paris, France: 1958.
-
- Benchelah A.-C., Bouziane H., Maka M. Fleurs du Sahara, arbres et arbustes, voyage au coeur de leurs usages avec les Touaregs du Tassili. Phytothérapie. 2004;2:191–197. doi: 10.1007/s10298-004-0052-z. - DOI
-
- Bellakhdar J. Plantes Médicinales au Maghreb et Soins de Base. Précis de Phytothérapie Moderne. Editions le Fennec; Casablanca, Morocco: 2006. 386p
-
- Baba Aissa F. Encyclopédie des Plantes Utiles. EDAS; Leonia, NJ, USA: 1999.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

