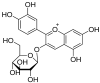
A Review of the Role of an Anthocyanin, Cyanidin-3- O- β-glucoside in Obesity-Related Complications
- PMID: 38005786
- PMCID: PMC10675560
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223889
A Review of the Role of an Anthocyanin, Cyanidin-3- O- β-glucoside in Obesity-Related Complications
Abstract
Obesity has become a major health issue worldwide and obese individuals possess higher levels of adipose tissue when compared with healthy individuals. Obesity is highly associated with the development of different chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, cancers, etc. Previous studies established that anthocyanin compounds play an important role in attenuating obesity-related consequences. Among various anthocyanin compounds, cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside (C3G) is the most important component and is widely distributed in various colored edible plant materials, especially berries, cherries, black rice, purple corn, etc. In recent decades, several studies have reported the therapeutical properties of C3G. C3G has various biological properties and health benefits, such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, anti-obesity, neuroprotective, anticancer, etc. In this review, we summarized the in vitro and in vivo studies in relation to the role of C3G in obesity-related complications. Several mechanistic studies demonstrated that C3G maintains the metabolism of glucose, fatty acids, and lipids by regulating different genes and signaling pathways. It could be concluded that the consumption of C3G protects healthy individuals from obesity-related issues by maintaining body weight and regulating their metabolism and energy balance. This review provides some important signaling pathways/targets of C3G to facilitate the prevention and treatment of obesity, leading to the development of important food supplements.
Keywords: adipocyte; adipogenesis; anthocyanin; cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside; cyanidin-3-glucoside; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Q., Vital D.L., Mejia E.G.D. Anthocyanins from colored maize ameliorated the inflammatory paracrine interplay between macrophages and adipocytes through regulation of NF-κB and JNK-dependent MAPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods. 2019;54:175–186. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.016. - DOI
-
- Xu H., Liu M., Liu H., Zhao B., Zheng M., Liu J. Anthocyanins from purple corn ameliorated obesity in high fat diet-induced obese mice through activating hepatic AMPK. J. Funct. Foods. 2021;84:104582. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104582. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources