Time-Dependent Proteomic Signatures Associated with Embryogenic Callus Induction in Carica papaya L
- PMID: 38005788
- PMCID: PMC10675192
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12223891
Time-Dependent Proteomic Signatures Associated with Embryogenic Callus Induction in Carica papaya L
Abstract
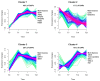
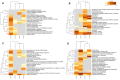
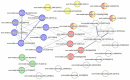
Sex segregation increases the cost of Carica papaya production through seed-based propagation. Therefore, in vitro techniques are an attractive option for clonal propagation, especially of hermaphroditic plants. Here, we performed a temporal analysis of the proteome of C. papaya calli aiming to identify the key players involved in embryogenic callus formation. Mature zygotic embryos used as explants were treated with 20 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid to induce embryogenic callus. Total proteins were extracted from explants at 0 (zygotic embryo) and after 7, 14, and 21 days of induction. A total of 1407 proteins were identified using a bottom-up proteomic approach. The clustering analysis revealed four distinct patterns of protein accumulation throughout callus induction. Proteins related to seed maturation and storage are abundant in the explant before induction, decreasing as callus formation progresses. Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolisms, aerobic respiration, and protein catabolic processes were enriched throughout days of callus induction. Protein kinases associated with auxin responses, such as SKP1-like proteins 1B, accumulated in response to callus induction. Additionally, regulatory proteins, including histone deacetylase (HD2C) and argonaute 1 (AGO1), were more abundant at 7 days, suggesting their role in the acquisition of embryogenic competence. Predicted protein-protein networks revealed the regulatory role of proteins 14-3-3 accumulated during callus induction and the association of proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation and hormone response. Our findings emphasize the modulation of the proteome during embryogenic callus initiation and identify regulatory proteins that might be involved in the activation of this process.
Keywords: Carica papaya; bottom-up proteomics; embryogenic callus; micropropagation; somatic embryos; time-series analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Salinas I., Salehi M., Hueso J.J., Cuevas J. Assessment of two sex-determining procedures in ‘BH-65’ papaya from an economical and developmental point of view. Fruits. 2018;73:184–190. doi: 10.17660/th2018/73.3.5. - DOI
-
- Xavier L., Almeida F.A., Pinto V.B., Silveira V. Large-scale regeneration of hermaphrodite emblings of Carica papaya L. Golden using early molecular sex determination during embryogenic callus multiplication. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2021;146:643–649. doi: 10.1007/s11240-021-02085-4. - DOI
-
- Gouvea D.S., Chagas K., Cipriano J.L.D., Lopes J.C., Schmildt E.R., Otoni W.C., Schmildt O., Araujo C.P.D., Alexandre R.S. Somatic embryogenesis in the commercial papaya hybrid UENF/Caliman 01 relying on plantlet production from sexed adult hermaphrodite donor plants. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019;91:e20180504. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201920180504. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almeida F.A., Vale E.M., Reis R.S., Santa-Catarina C., Silveira V. LED lamps enhance somatic embryo maturation in association with the differential accumulation of proteins in the Carica papaya L. ‘Golden’ embryogenic callus. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019;143:109–118. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.08.029. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- E-26/211.310/2021/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- Proc E26/200.999/2021/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- 307755/2019-3/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- Finance Code 001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

