G-Quadruplexes in the Viral Genome: Unlocking Targets for Therapeutic Interventions and Antiviral Strategies
- PMID: 38005893
- PMCID: PMC10674748
- DOI: 10.3390/v15112216
G-Quadruplexes in the Viral Genome: Unlocking Targets for Therapeutic Interventions and Antiviral Strategies
Abstract
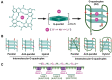
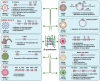
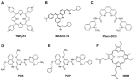
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are unique non-canonical four-stranded nucleic acid secondary structures formed by guanine-rich DNA or RNA sequences. Sequences with the potential to form quadruplex motifs (pG4s) are prevalent throughout the genomes of all organisms, spanning from prokaryotes to eukaryotes, and are enriched within regions of biological significance. In the past few years, the identification of pG4s within most of the Baltimore group viruses has attracted increasing attention due to their occurrence in regulatory regions of the genome and the subsequent implications for regulating critical stages of viral life cycles. In this context, the employment of specific G4 ligands has aided in comprehending the intricate G4-mediated regulatory mechanisms in the viral life cycle, showcasing the potential of targeting viral G4s as a novel antiviral strategy. This review offers a thorough update on the literature concerning G4s in viruses, including their identification and functional significance across most of the human-infecting viruses. Furthermore, it delves into potential therapeutic avenues targeting G4s, encompassing various G4-binding ligands, G4-interacting proteins, and oligonucleotide-based strategies. Finally, the article highlights both progress and challenges in the field, providing valuable insights into leveraging this unusual nucleic acid structure for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; G-quadruplex forming sequences; G-quadruplex ligands; G4-interacting proteins; antiviral activity; non-canonical G4s; oligonucleotides; small-molecule drugs; targeting G4s; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An insight into G-quadruplexes: Identification and potential therapeutic targets in livestock viruses.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 5;279:116848. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116848. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39255642 Review.
-
Unlocking G-Quadruplexes as Antiviral Targets.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jul;73(3):897-923. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000230. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34045305 Review.
-
G-Quadruplex Targeting in the Fight against Viruses: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 12;22(20):10984. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010984. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-Quadruplexes in the Regulation of Viral Gene Expressions and Their Impacts on Controlling Infection.Pathogens. 2024 Jan 8;13(1):60. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010060. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38251367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-quadruplexes and G-quadruplex ligands: targets and tools in antiviral therapy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Apr 20;46(7):3270-3283. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky187. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29554280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond the Pandemic Era: Recent Advances and Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Against Emerging Variants of Concern.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Apr 17;13(4):424. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13040424. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40333293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Compendium of G-Flipon Biological Functions That Have Experimental Validation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 25;25(19):10299. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910299. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Epigenetics: Innovative Approaches in Diagnosing and Combating Viral Acute Respiratory Infections.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 1;14(2):129. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020129. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spotlight on G-Quadruplexes: From Structure and Modulation to Physiological and Pathological Roles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 9;25(6):3162. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA G-quadruplexes: emerging regulators of gene expression and therapeutic targets.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):143. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01656-4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40608121 Review.
References
-
- Beaume N., Pathak R., Yadav V.K., Kota S., Misra H.S., Gautam H.K., Chowdhury S. Genome-wide study predicts promoter-G4 DNA motifs regulate selective functions in bacteria: Radioresistance of D. radiodurans involves G4 DNA-mediated regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:76–89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

