SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a-Mediated NF-κB Activation Is Not Dependent on TRAF-Binding Sequence
- PMID: 38005906
- PMCID: PMC10675646
- DOI: 10.3390/v15112229
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a-Mediated NF-κB Activation Is Not Dependent on TRAF-Binding Sequence
Abstract
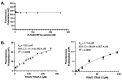
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused a global pandemic of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Excessive inflammation is a hallmark of severe COVID-19, and several proteins encoded in the SARS-CoV-2 genome are capable of stimulating inflammatory pathways. Among these, the accessory protein open reading frame 3a (ORF3a) has been implicated in COVID-19 pathology. Here we investigated the roles of ORF3a in binding to TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) proteins and inducing nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation. X-ray crystallography and a fluorescence polarization assay revealed low-affinity binding between an ORF3a N-terminal peptide and TRAFs, and a dual-luciferase assay demonstrated NF-κB activation by ORF3a. Nonetheless, mutation of the N-terminal TRAF-binding sequence PIQAS in ORF3a did not significantly diminish NF-κB activation in our assay. Our results thus suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 protein may activate NF-κB through alternative mechanisms.
Keywords: NF-κB; SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a; TRAF proteins; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a Protein as a Therapeutic Target against COVID-19 and Long-Term Post-Infection Effects.Pathogens. 2024 Jan 14;13(1):75. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010075. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38251382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a positively regulates NF-κB activity by enhancing IKKβ-NEMO interaction.Virus Res. 2023 Apr 15;328:199086. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199086. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36894068 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-κB and induction of proinflammatory cytokine expressions mediated by ORF7a protein of SARS-CoV-2.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 29;11(1):13464. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92941-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34188167 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a induces COVID-19-associated kidney injury through HMGB1-mediated cytokine production.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0230824. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02308-24. Epub 2024 Sep 30. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39345136 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Pathogens. 2024 Feb 12;13(2):164. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13020164. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38392902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Highly ordered clustering of TNFα and BAFF ligand-receptor-intracellular adaptor complexes on a lipid membrane.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5551. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61271-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593711 Free PMC article.
-
A live attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine constructed by dual inactivation of NSP16 and ORF3a.EBioMedicine. 2025 Apr;114:105662. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105662. Epub 2025 Mar 24. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40132472 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a Protein as a Therapeutic Target against COVID-19 and Long-Term Post-Infection Effects.Pathogens. 2024 Jan 14;13(1):75. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010075. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38251382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Karki R., Sharma B.R., Tuladhar S., Williams E.P., Zalduondo L., Samir P., Zheng M., Sundaram B., Banoth B., Malireddi R.K.S., et al. Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes. Cell. 2021;184:149–168.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

