Integrase Defective Lentiviral Vector Promoter Impacts Transgene Expression in Target Cells and Magnitude of Vector-Induced Immune Responses
- PMID: 38005931
- PMCID: PMC10674321
- DOI: 10.3390/v15112255
Integrase Defective Lentiviral Vector Promoter Impacts Transgene Expression in Target Cells and Magnitude of Vector-Induced Immune Responses
Abstract
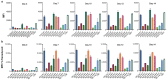
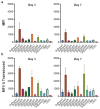
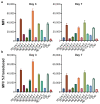
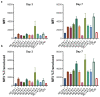
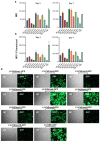
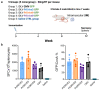
Integrase defective lentiviral vectors (IDLVs) are a promising vaccine delivery platform given their ability to induce high magnitude and durable antigen-specific immune responses. IDLVs based on the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) are significantly more efficient at transducing human and simian dendritic cells (DCs) compared to HIV-based vectors, resulting in a higher expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. Additionally, IDLV persistence and continuous antigen expression in muscle cells at the injection site contributes to the durability of the vaccine-induced immune responses. Here, to further optimize transgene expression levels in both DCs and muscle cells, we generated ten novel lentiviral vectors (LVs) expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under different hybrid promoters. Our data show that three of the tested hybrid promoters resulted in the highest transgene expression levels in mouse DCs, monkey DCs and monkey muscle cells. We then used the three LVs with the highest in vitro transgene expression levels to immunize BALB/c mice and observed high magnitude T cell responses at 3 months post-prime. Our study demonstrates that the choice of the vector promoter influences antigen expression levels in target cells and the ensuing magnitude of T cell responses in vivo.
Keywords: antigen expression; dendritic cells; immune responses; lentiviral vectors; muscle cells; vector promoter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

