The Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Future Vaccine Synthesis
- PMID: 38005963
- PMCID: PMC10675160
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11111631
The Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Future Vaccine Synthesis
Abstract
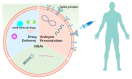
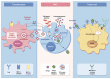
Vaccines have significant potential in treating and/or preventing diseases, yet there remain challenges in developing effective vaccines against some diseases, such as AIDS and certain tumors. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), a subset of cells with low immunogenicity, high proliferation potential, and an abundant source of extracellular vesicles (EVs), represent one of the novel and promising vaccine platforms. This review describes the unique features and potential mechanisms of MSCs as a novel vaccine platform. We also cover aspects such as the safety and stability of MSCs that warrant future in-depth studies.
Keywords: EVs; anti-cancer; antigen delivery; mesenchymal stem cells; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles: A promising nanomedicine for drug delivery system.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;203:115167. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115167. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35820499 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Potential roles in rheumatic diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2020 Jul 26;12(7):688-705. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.688. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32843922 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles: regenerative and immunomodulatory effects and potential applications in sepsis.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Oct;374(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2871-5. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29955951 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and MSCs-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Infectious Diseases: From Basic Research to Clinical Practice.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;9(11):662. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9110662. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells be a potential therapy for acute pancreatitis-induced cardiac injury?World J Stem Cells. 2023 Jul 26;15(7):654-664. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i7.654. World J Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37545754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategic Advances in Targeted Delivery Carriers for Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 17;26(14):6879. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146879. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Anti-Tumor Efficacy of DC-Based Vaccines Targeting TME-Associated Antigens Is Improved When Combined with a Chemokine-Modulating Regimen and/or Anti-PD-L1.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;12(7):777. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070777. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masalova O.V., Lesnova E.I., Klimova R.R., Momotyuk E.D., Kozlov V.V., Ivanova A.M., Payushina O.V., Butorina N.N., Zakirova N.F., Narovlyansky A.N., et al. Genetically Modified Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells Expressing Non-Structural Proteins of Hepatitis C Virus Induce Effective Immune Response. Vaccines. 2020;8:62. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8010062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

