In Vivo Treatment with Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Reduces CCR5 Expression on Vaccine-Induced Activated CD4+ T-Cells
- PMID: 38005994
- PMCID: PMC10675829
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11111662
In Vivo Treatment with Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Reduces CCR5 Expression on Vaccine-Induced Activated CD4+ T-Cells
Abstract
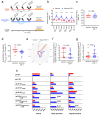
At the heart of the DNA/ALVAC/gp120/alum vaccine's efficacy in the absence of neutralizing antibodies is a delicate balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory immune responses that effectively decreases the risk of SIVmac251 acquisition in macaques. Vaccine efficacy is linked to antibodies recognizing the V2 helical conformation, DC-10 tolerogenic dendritic cells eliciting the clearance of apoptotic cells via efferocytosis, and CCR5 downregulation on vaccine-induced gut homing CD4+ cells. RAS activation is also linked to vaccine efficacy, which prompted the testing of IGF-1, a potent inducer of RAS activation with vaccination. We found that IGF-1 changed the hierarchy of V1/V2 epitope recognition and decreased both ADCC specific for helical V2 and efferocytosis. Remarkably, IGF-1 also reduced the expression of CCR5 on vaccine-induced CD4+ gut-homing T-cells, compensating for its negative effect on ADCC and efferocytosis and resulting in equivalent vaccine efficacy (71% with IGF-1 and 69% without).
Keywords: CCR5; CD4; HIV; IGF-1; SIV; T-cells; insulin-like growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS . In Danger: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS); Geneva, Switzerland: 2022. p. 373.
-
- Johnson & Johnson Johnson & Johnson and Global Partners Announce Results from Phase 2b Imbokodo HIV Vaccine Clinical Trial in Young Women in Sub-Saharan Africa. PR Newswire. Aug 31, 2021.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

