Antibody Profiling of Microbial Antigens in the Blood of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Recipients Using Microbial Protein Microarrays
- PMID: 38006026
- PMCID: PMC10674746
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11111694
Antibody Profiling of Microbial Antigens in the Blood of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Recipients Using Microbial Protein Microarrays
Abstract
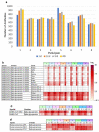
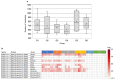
Although studies have demonstrated that infections with various viruses, bacteria, and parasites can modulate the immune system, no study has investigated changes in antibodies against microbial antigens after the COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. IgG antibodies against microbial antigens in the blood of vaccinees were comprehensively analyzed using microbial protein microarrays that carried approximately 5000 microbe-derived proteins. Changes in antibodies against microbial antigens were scrutinized in healthy participants enrolled in the Fukushima Vaccination Community Survey conducted in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, after their second and third COVID-19 mRNA vaccinations. Antibody profiling of six groups stratified by antibody titer and the remaining neutralizing antibodies was also performed to study the dynamics of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and the changes in antibodies against microbial antigens. The results showed that changes in antibodies against microbial antigens other than SARS-CoV-2 antigens were extremely limited after COVID-19 vaccination. In addition, antibodies against a staphylococcal complement inhibitor have been identified as microbial antigens that are associated with increased levels of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. These antibodies may be a predictor of the maintenance of neutralizing antibodies following the administration of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; antibody; bacteria; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Yudai Kaneko is employed by the company Medical & Biological Laboratories, Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan. MBL imported the testing material used in this research. Yurie Kobashi and Masaharu Tsubokura received a research grant from the Pfizer Health Research Foundation for research not associated with this work. Masaharu Tsubokura received a research grant from Moderna Inc. outside of this work. The remaining authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [(accessed on 5 September 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19.
-
- COVID-19 Vaccines. [(accessed on 5 September 2023)]. Available online: https://japan.kantei.go.jp/ongoingtopics/vaccine.html.
-
- Feikin D.R., Higdon M.M., Abu-Raddad L.J., Andrews N., Araos R., Goldberg Y., Groome M.J., Huppert A., O’Brien K.L., Smith P.G., et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: Results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet. 2022;399:924–944. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00152-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

