Systematic Review on the Efficacy, Effectiveness, Safety, and Immunogenicity of Monkeypox Vaccine
- PMID: 38006040
- PMCID: PMC10674429
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11111708
Systematic Review on the Efficacy, Effectiveness, Safety, and Immunogenicity of Monkeypox Vaccine
Abstract
Background: The variation in the reported vaccine safety and effectiveness could contribute to the high rates of vaccine hesitancy among the general population and healthcare workers in areas where monkeypox (mpox) is circulating. In this review, our objective was to evaluate the safety, immunogenicity, effectiveness, and efficacy of the mpox vaccines.
Methods: An extensive search for articles across multiple databases was performed, including searching six databases (PubMed Central, PubMed Medline, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane, ProQuest), two pre-print databases (European PMC Preprint and MedRxiv), and Google Scholar.
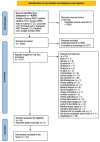
Results: A total of 4290 citations were retrieved from the included databases. Following the removal of duplicates and the initial screening of records, a total of 36 studies were included into the analysis. Additionally, we identified five more studies through manual searches, resulting in a total of 41 eligible articles for qualitative synthesis. The study findings revealed that mpox vaccines demonstrate the ability to generate adequate antibodies; however, their effectiveness may decrease over time, exhibiting varying safety profiles. Most of the included studies consistently reported substantial levels of effectiveness and efficacy against mpox. Interestingly, the number of vaccine doses administered was found to influence the degree of immunogenicity, subsequently impacting the overall effectiveness and efficacy of the vaccines. Furthermore, we found that smallpox vaccines exhibited a form of cross-protection against mpox.
Conclusions: Vaccines can be used to prevent mpox and effectively control its spread.
Keywords: monkeypox; vaccine effectiveness; vaccine efficacy; vaccine immunogenicity; vaccine safety.
Conflict of interest statement
We do not have conflict of interest associated with this publication, and there has been no financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. This manuscript is original, has not been previously published, and is not currently under consideration by another journal.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Mpox Outbreak. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/mpox.
-
- World Health Organization 2022–2023 Mpox (Monkeypox) Outbreak: Global Trends. 2023. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global/
-
- World Health Organization Fifth Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR) Emergency Committee on the Multi-Country Outbreak of Mpox (Monkeypox) 2023. [(accessed on 25 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-05-2023-fifth-meeting-of-the-internatio...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources