Association of Maternal Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccination within 3 Months before Conception with Neonatal Outcomes
- PMID: 38006042
- PMCID: PMC10674970
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11111710
Association of Maternal Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccination within 3 Months before Conception with Neonatal Outcomes
Abstract
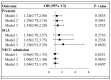
There is limited available data addressing whether inactivated COVID-19 vaccination before conception is associated with adverse neonatal outcomes. This cohort study included all singleton live births at our center from March 1 to June 30, 2022. According to whether a maternal inactivated COVID-19 vaccination had been administered within 3 months before conception or not, neonates were identified as being in the vaccinated or unvaccinated group. Vaccination information and clinical characteristics were extracted for analysis. Furthermore, neonatal outcomes were analyzed and compared between these two groups in the present study. The cohort included 856 eligible newborns, of whom 369 were exposed to maternal vaccination before conception and 487 were unexposed newborns. No differences were observed in rates of preterm birth, newborns being small for gestational age, or neonatal intensive care unit admission between exposed and unexposed newborns. Furthermore, even after adjusting for social-economic status and maternal characteristics, there remained no significant differences in these neonatal outcomes. Our study revealed no statistically significant differences between newborns born to women who received inactivated vaccines prior to conception compared with those who did not receive any vaccinations. In addition, our study also highlights the importance of considering COVID-19 vaccination before conception.
Keywords: COVID-19; NICU admission; preterm birth; small for gestational age; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccination During Pregnancy With Neonatal and Early Infant Outcomes.JAMA Pediatr. 2022 May 1;176(5):470-477. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.0001. JAMA Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35142809 Free PMC article.
-
Reductions in stillbirths and preterm birth in COVID-19-vaccinated women: a multicenter cohort study of vaccination uptake and perinatal outcomes.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 May;228(5):585.e1-585.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.10.040. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36336084 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy outcomes following natural conception and assisted reproduction treatment in women who received COVID-19 vaccination prior to conception: a population-based cohort study in China.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 11;10:1250165. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1250165. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37886353 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of neonatal outcomes of COVID-19 vaccination in pregnancy.Pediatr Res. 2023 Jul;94(1):34-42. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02421-0. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36596943 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of COVID-19 vaccination in pregnant women and their neonatal outcome: a narrative Review.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(1):2183750. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2183750. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 36906793
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness and Influence of COVID-19 Vaccination on Perinatal Individuals and Their Newborns: An Updated Meta-Analysis.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025 Jun 24;2025:6115890. doi: 10.1155/cjid/6115890. eCollection 2025. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40599303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 vaccination and birth outcomes of 186,990 women vaccinated before pregnancy: an England-wide cohort study.Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024 Aug 13;45:101025. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2024.101025. eCollection 2024 Oct. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024. PMID: 39974773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) [(accessed on 30 July 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- World Health Organization Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—27 July 2023. [(accessed on 30 July 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and Efficacy of the Chadox1 Ncov-19 Vaccine (Azd1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An Interim Analysis of Four Randomised Controlled Trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

