Preparation and Space Charge Properties of Functionalized Zeolite/Crosslinked Polyethylene Composites with High Thermal Conductivity
- PMID: 38006087
- PMCID: PMC10674397
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15224363
Preparation and Space Charge Properties of Functionalized Zeolite/Crosslinked Polyethylene Composites with High Thermal Conductivity
Abstract
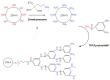
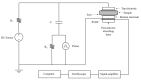
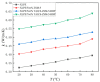
Nanocomposite doping is an effective method to improve the dielectric properties of polyethylene. Meanwhile, the introduction of thermal conductivity groups in crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) is also an effective way to improve the thermal conductivity. Nano-zeolite is an inorganic material with a porous structure that can be doped into polyethylene to improve the insulation performance. In this paper, hyperbranched polyarylamide (HBP) with a high thermal conductivity and an auxiliary crosslinking agent (TAIC) was grafted on the surface of ZSM-5 nano-zeolite successively to obtain functionalized nano-zeolite (TAICS-ZSM-5-HBP) (the "S" in TAICS means plural). The prepared functionalized nano-zeolite was doped in polyethylene and grafted under a thermal crosslinking reaction to prepare nanocomposites (XLPE/TAICS-ZSM-5-HBP). The structural characterization showed that the nanocomposite was successfully prepared and that the nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed in the polyethylene matrix. The space charge of the TAICS-ZSM-5-HBP 5wt% nanocomposite under a high electric field was obviously inhibited. The space charge short-circuit test showed that the porous structure of the nano-zeolite introduced more deep traps, which made the trapped charge difficult to break off, hindering the charge injection. The introduction of TAICS-ZSM-5-HBP particles can greatly improve the thermal conductivity of nanocomposites. The thermal conductivity of the XLPE/5wt% and XLPE/7wt% TAICS-ZSM-5-HBP nanocomposites increased by 42.21% and 69.59% compared to that of XLPE at 20 °C, and by 34.27% and 62.83% at 80 °C.
Keywords: crosslinked polyethylene; dielectric properties; space charge; thermal conductivity; zeolite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Functionalization of Silica Nanoparticles to Improve Crosslinking Degree, Insulation Performance and Space Charge Characteristics of UV-initiated XLPE.Molecules. 2020 Aug 20;25(17):3794. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173794. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32825451 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Nanoporous Molecular Sieves TS-1 on Electrical Properties of Crosslinked Polyethylene Nanocomposites.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jun 6;14(11):985. doi: 10.3390/nano14110985. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38869610 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Structure and Dielectric Properties of Zeolite/LDPE Nanocomposite under Thermal Aging.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Sep 16;12(9):2108. doi: 10.3390/polym12092108. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32947923 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of Polymer Composites Used in High-Voltage Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2016 Apr 28;8(5):173. doi: 10.3390/polym8050173. Polymers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30979265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative approaches for augmenting dielectric properties in cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE): A review.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 22;10(15):e34737. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34737. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou Y., Peng S., Hu J., He J. Polymeric insulation materials for HVDC cables: Development, challenges and future perspective. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017;24:1308–1318. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2017.006205. - DOI
-
- Demin T. A survey of development in HVDC XLPE cable. J. Electr. Electron. Educ. 2001;23:5–10.
-
- Huang X.Y., Zhang J., Jiang P.K. Thermoplastic power cable insulation materials: History and development. High Volt. Eng. 2018;44:1377–1398.
-
- Yang P., He M., Ren X., Zhou K. Effect of carbon nanotube on space charge suppression in PP/EPDM/CNT nanocomposites. J. Polym. Res. 2020;27:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s10965-020-02107-3. - DOI
-
- Sun L., Zhang P., Li Z., Zhang R., Fu M., Hou S. Silicone rubber-based nonlinear composites for HVDC cable termination. High Volt. Eng. 2019;45:1654–1665.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

