Membrane extraction in native lipid nanodiscs reveals dynamic regulation of Cdc42 complexes during cell polarization
- PMID: 38006206
- PMCID: PMC11947473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.11.021
Membrane extraction in native lipid nanodiscs reveals dynamic regulation of Cdc42 complexes during cell polarization
Abstract
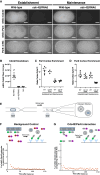
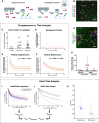
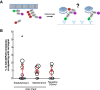
Embryonic development requires the establishment of cell polarity to enable cell fate segregation and tissue morphogenesis. This process is regulated by Par complex proteins, which partition into polarized membrane domains and direct downstream polarized cell behaviors. The kinase aPKC (along with its cofactor Par6) is a key member of this network and can be recruited to the plasma membrane by either the small GTPase Cdc42 or the scaffolding protein Par3. Although in vitro interactions among these proteins are well established, much is still unknown about the complexes they form during development. Here, to enable the study of membrane-associated complexes ex vivo, we used a maleic acid copolymer to rapidly isolate membrane proteins from single C. elegans zygotes into lipid nanodiscs. We show that native lipid nanodisc formation enables detection of endogenous complexes involving Cdc42, which are undetectable when cells are lysed in detergent. We found that Cdc42 interacts more strongly with aPKC/Par6 during polarity maintenance than polarity establishment, two developmental stages that are separated by only a few minutes. We further show that Cdc42 and Par3 do not bind aPKC/Par6 simultaneously, confirming recent in vitro findings in an ex vivo context. Our findings establish a new tool for studying membrane-associated signaling complexes and reveal an unexpected mode of polarity regulation via Cdc42.
Copyright © 2023 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Polarity protein Par6 facilitates the processive phosphorylation of Lgl via a dynamic interaction with aPKC.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 1;8(1):967. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08401-4. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40595028 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Chromokinesin Klp-19 regulates microtubule overlap and dynamics during anaphase in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 31:2023.10.26.564275. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.26.564275. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37961478 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Atypical Protein Kinase C Promotes its own Asymmetric Localisation by Phosphorylating Cdc42 in the C. elegans zygote.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 14:2023.10.27.563985. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.27.563985. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38009101 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Quantitative perturbation-phenotype maps reveal nonlinear responses underlying robustness of PAR-dependent asymmetric cell division.PLoS Biol. 2024 Dec 9;22(12):e3002437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002437. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39652540 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomerization and positive feedback on membrane recruitment encode dynamically stable PAR-3 asymmetries in the C. elegans zygote.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 28:2023.08.04.552031. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.04.552031. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39253498 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Apical PAR protein caps orient the mitotic spindle in C. elegans early embryos.Curr Biol. 2023 Oct 23;33(20):4312-4329.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.069. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37729910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joberty G., Petersen C., et al. Macara I.G. The cell-polarity protein Par6 links Par3 and atypical protein kinase C to Cdc42. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:531–539. - PubMed
-
- Lin D., Edwards A.S., et al. Pawson T. A mammalian PAR-3-PAR-6 complex implicated in Cdc42/Rac1 and aPKC signalling and cell polarity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:540–547. - PubMed
-
- Qiu R.G., Abo A., Steven Martin G. A human homolog of the C. elegans polarity determinant Par-6 links Rac and Cdc42 to PKCζ signaling and cell transformation. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:697–707. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

