Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and application of nano-therapeutics as a promising approach to combat methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 38006316
- PMCID: PMC11221481
- DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2023.2285187
Staphylococcus aureus epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and application of nano-therapeutics as a promising approach to combat methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
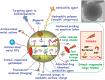
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium and one of the most prevalent infectious disease-related causes of morbidity and mortality in adults. This pathogen can trigger a broad spectrum of diseases, from sepsis and pneumonia to severe skin infections that can be fatal. In this review, we will provide an overview of S. aureus and discuss the extensive literature on epidemiology, transmission, genetic diversity, evolution and antibiotic resistance strains, particularly methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA). While many different virulence factors that S. aureus produces have been investigated as therapeutic targets, this review examines recent nanotechnology approaches, which employ materials with atomic or molecular dimensions and are being used to diagnose, treat, or eliminate the activity of S. aureus. Finally, having a deeper understanding and clearer grasp of the roles and contributions of S. aureus determinants, antibiotic resistance, and nanotechnology will aid us in developing anti-virulence strategies to combat the growing scarcity of effective antibiotics against S. aureus.
Keywords: MDR; Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance; mesoporous silica nanoparticles; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):547-569. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1878688. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33522395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigational drugs to treat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016;25(1):73-93. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2016.1109077. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26536498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence Factor Targeting of the Bacterial Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus for Vaccine and Therapeutics.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(2):111-127. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666161128123536. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 27894236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different sampling strategies for optimal detection of the overall genetic diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0014024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00140-24. Epub 2024 May 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38809050 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors and genetic characteristics of methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Myanmar.Microb Drug Resist. 2011 Dec;17(4):525-35. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2011.0061. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Microb Drug Resist. 2011. PMID: 21834665
Cited by
-
A Stroll Through Saffron Fields, Cannabis Leaves, and Cherry Reveals the Path to Waste-Derived Antimicrobial Bioproducts.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;18(7):1003. doi: 10.3390/ph18071003. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732292 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome analysis of a ST45-SCCmec IVa (2B)-t116 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain isolated from the sputum of a 5-year-old child with pneumonia.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 21;14:1413024. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1413024. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39906210 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) in Staphylococcus aureus: Prevalence, Molecular Mechanisms, and Public Health Implications.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;17(7):323. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070323. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing Etalocib suppresses multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by disrupting the bacterial membrane.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04163-5. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40750851 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal Drug Resistance: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Nanoparticle Interventions.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Feb 19;18:1007-1033. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S510024. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39990781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boswihi SS, Udo EE. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an update on the epidemiology, treatment options and infection control. Curr Med Res Pract. 2018;8(1):18–24. InternetAvailable from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S23520.... doi: 10.1016/j.cmrp.2018.01.001 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
