Effect of data harmonization of multicentric dataset in ASD/TD classification
- PMID: 38006422
- PMCID: PMC10676338
- DOI: 10.1186/s40708-023-00210-x
Effect of data harmonization of multicentric dataset in ASD/TD classification
Abstract
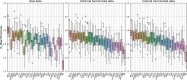
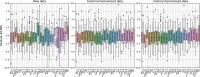
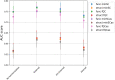
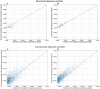
Machine Learning (ML) is nowadays an essential tool in the analysis of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) data, in particular in the identification of brain correlates in neurological and neurodevelopmental disorders. ML requires datasets of appropriate size for training, which in neuroimaging are typically obtained collecting data from multiple acquisition centers. However, analyzing large multicentric datasets can introduce bias due to differences between acquisition centers. ComBat harmonization is commonly used to address batch effects, but it can lead to data leakage when the entire dataset is used to estimate model parameters. In this study, structural and functional MRI data from the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) collection were used to classify subjects with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) compared to Typical Developing controls (TD). We compared the classical approach (external harmonization) in which harmonization is performed before train/test split, with an harmonization calculated only on the train set (internal harmonization), and with the dataset with no harmonization. The results showed that harmonization using the whole dataset achieved higher discrimination performance, while non-harmonized data and harmonization using only the train set showed similar results, for both structural and connectivity features. We also showed that the higher performances of the external harmonization are not due to larger size of the sample for the estimation of the model and hence these improved performance with the entire dataset may be ascribed to data leakage. In order to prevent this leakage, it is recommended to define the harmonization model solely using the train set.
Keywords: ABIDE; Autism spectrum disorder; Harmonization; Machine learning; Multi-site data.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Connectivity-Based Prediction of Autism on Site Harmonized ABIDE Dataset.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021 Dec;68(12):3628-3637. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3080259. Epub 2021 Nov 19. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 33989150 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-site harmonization of MRI data uncovers machine-learning discrimination capability in barely separable populations: An example from the ABIDE dataset.Neuroimage Clin. 2022;35:103082. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103082. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Neuroimage Clin. 2022. PMID: 35700598 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning based joint fusion approach to exploit anatomical and functional brain information in autism spectrum disorders.Brain Inform. 2024 Jan 9;11(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40708-023-00217-4. Brain Inform. 2024. PMID: 38194126 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning in Large and Multi-Site Structural Brain MR Imaging Datasets.Front Neuroinform. 2022 Jan 20;15:805669. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2021.805669. eCollection 2021. Front Neuroinform. 2022. PMID: 35126080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AIMAFE: Autism spectrum disorder identification with multi-atlas deep feature representation and ensemble learning.J Neurosci Methods. 2020 Sep 1;343:108840. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108840. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Neurosci Methods. 2020. PMID: 32653384 Review.
References
-
- Guze Samuel B. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV) Am J Psychiatry. 1995;152(8):1228–1228. doi: 10.1176/ajp.152.8.122. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization: The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders : diagnostic criteria for research. World Health Organization (1993)
-
- Postema M, Van Rooij D, Anagnostou E, Arango C, Auzias G, Behrmann M, Busatto G, Calderoni S, Calvo R, Daly E, Deruelle C, Di Martino A, Dinstein I, Duran F, Durston S, Ecker C, Ehrlich S, Fair D, Fedor J, Francks C. Altered structural brain asymmetry in autism spectrum disorder in a study of 54 datasets. Nat Commun. 2019 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13005-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

