Protective effects of apigenin on the brain transcriptome with aging
- PMID: 38007051
- PMCID: PMC10843586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2023.111889
Protective effects of apigenin on the brain transcriptome with aging
Abstract
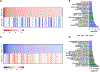
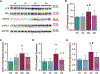
Brain aging is associated with reduced cognitive function that increases the risk for dementia. Apigenin is a bioactive plant compound that inhibits cellular aging processes and could protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction, but its mechanisms of action in the brain have not been comprehensively studied. We characterized brain transcriptome changes in young and old mice treated with apigenin in drinking water. We observed improved learning/memory in old treated mice, and our transcriptome analyses indicated that differentially expressed genes with aging and apigenin were primarily related to immune responses, inflammation, and cytokine regulation. Moreover, we found that genes/transcripts that were increased in old vs. young mice but downregulated with apigenin treatment in old animals were associated with immune activation/inflammation, whereas transcripts that were reduced with aging but increased with apigenin were related neuronal function and signaling. We also found that these transcriptome differences with aging and apigenin treatment were driven in part by glial cells. To follow up on these in vivo transcriptome findings, we studied aged astrocytes in vitro, and we found that apigenin reduced markers of inflammation and cellular senescence in these cells. Collectively, our data suggest that apigenin may protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction by suppressing neuro-inflammatory processes.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Brain aging; Cognitive decline; Neuroinflammation; Transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
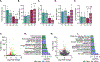
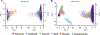
Similar articles
-
Exploring the Role of Apigenin in Neuroinflammation: Insights and Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 6;25(9):5041. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095041. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apigenin restores endothelial function by ameliorating oxidative stress, reverses aortic stiffening, and mitigates vascular inflammation with aging.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):H185-H196. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00118.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34114892 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin Ameliorates Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction and Neuronal Damage in Mice.Molecules. 2021 Aug 27;26(17):5192. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175192. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500626 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent hippocampal induction of MHC II pathway components and glial activation with advanced aging is not correlated with cognitive impairment.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Oct 11;8:138. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-138. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21989322 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes in the aging brain express characteristics of senescence-associated secretory phenotype.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Jul;34(1):3-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07738.x. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21649759 Review.
Cited by
-
Widely Targeted Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Nutritional Potential of Yellowhorn (Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge) Leaves and Flowers.Foods. 2024 Apr 21;13(8):1274. doi: 10.3390/foods13081274. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38672945 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin: a natural molecule at the intersection of sleep and aging.Front Nutr. 2024 Feb 27;11:1359176. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1359176. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38476603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Role of Apigenin in Neuroinflammation: Insights and Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 6;25(9):5041. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095041. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiorgan transcriptomics in mice identifies immunoglobulin heavy constant mu (Ighm) as a tissue-level aging biomarker.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 15;122(28):e2423142122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2423142122. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40643973
-
Characterization and Anti-Aging Potency of Phenolic Compounds in Xianhu Tea Extracts.Foods. 2025 Feb 21;14(5):737. doi: 10.3390/foods14050737. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anusha C, Sumathi T and Joseph LD, 2017. Protective role of apigenin on rotenone induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Suppression of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress mediated apoptosis. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 269, 67–79. - PubMed
-
- Balez R, Steiner N, Engel M, Muñoz SS, Lum JS, Wu Y, Wang D, Vallotton P, Sachdev P, O’Connor M, Sidhu K, Münch G and Ooi L, 2016. Neuroprotective effects of apigenin against inflammation, neuronal excitability and apoptosis in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 6, 31450. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

