Sulforaphane alleviates psoriasis by enhancing antioxidant defense through KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway activation and attenuating inflammatory signaling
- PMID: 38007430
- PMCID: PMC10676357
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06234-9
Sulforaphane alleviates psoriasis by enhancing antioxidant defense through KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway activation and attenuating inflammatory signaling
Abstract
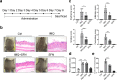
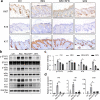
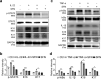
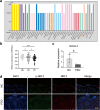
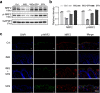
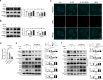
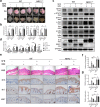
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Sulforaphane (SFN) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. In this study, we investigated the effects of SFN on a mouse model of psoriasis induced by imiquimod (IMQ) and its underlying molecular mechanism. Mice treated with SFN showed significant improvement in psoriatic symptoms, including reduced erythema, scales, and cutaneous thickness. Histopathological analysis and immunohistochemical staining revealed decreased expression of K16, K17, and Ki67 in SFN-treated mice, indicating reduced abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes and cutaneous inflammation. SFN treatment also reduced the activation of STAT3 and NF-κB pathways and downregulated pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and CCL2. In vitro experiments using HaCaT cells demonstrated that SFN inhibited IL-22 and TNF-α-induced activation of inflammatory pathways and keratinocyte proliferation. Network pharmacology analysis suggested that the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway might be involved in the protective effects of SFN on psoriasis. We observed reduced NRF2 expression in human psoriatic lesions, and subsequent experiments showed that SFN activated KEAP1-NRF2 pathway in vivo and in vitro. Importantly, NRF2-deficient mice exhibited aggravated psoriasis-like symptoms and reduced response to SFN treatment. Our findings indicate that SFN ameliorates psoriasis symptoms and inflammation through the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway, suggesting a potential therapeutic role for SFN in the treatment of psoriasis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gentiopicroside ameliorates psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting keratinocyte activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May;46(5):1361-1374. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01449-8. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39779965
-
Rutin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions by inhibiting oxidative stress injury and the inflammatory response in mice via the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08451-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596643 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Activation of CB2R Ameliorates Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Inflammation. 2023 Aug;46(4):1255-1271. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01805-6. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 37000322
-
Sulforaphane and ophthalmic diseases.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 May 22;12(8):5296-5311. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4230. eCollection 2024 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39139965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The KEAP1/NRF2 Signaling Pathway in Keratinization.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;9(8):751. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080751. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-Released Growth Factors (PRGFs) Activate NRF2-ARE and Modulate Inflammatory Response in an NRF2-Dependent Manner in Primary Human Keratinocytes.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 May;24(5):e70228. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70228. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40353553 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane relieved inflammation symptoms in EAP mice by blocking oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the Nrf2 pathway.Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jan 21;219(1):uxaf022. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxaf022. Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40207573
-
Unveiling ferroptosis: a new frontier in skin disease research.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 4;15:1485523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485523. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39430757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gentiopicroside ameliorates psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting keratinocyte activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May;46(5):1361-1374. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01449-8. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39779965
-
Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jul 11;20(1):20251139. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1139. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40667480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan AQ, Rashid K, AlAmodi AA, Agha MV, Akhtar S, Hakeem I, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancer pathogenesis and therapy: an update on the role of ROS in anticancer action of benzophenanthridine alkaloids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112142. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112142. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

