Modulation of cell cycle increases CRISPR-mediated homology-directed DNA repair
- PMID: 38007480
- PMCID: PMC10676593
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-023-01159-4
Modulation of cell cycle increases CRISPR-mediated homology-directed DNA repair
Abstract
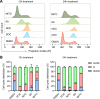
Background: Gene knock-in (KI) in animal cells via homology-directed repair (HDR) is an inefficient process, requiring a laborious work for screening from few modified cells. HDR tends to occur in the S and G2/M phases of cell cycle; therefore, strategies that enhance the proportion of cells in these specific phases could improve HDR efficiency.
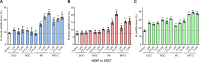
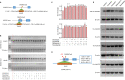
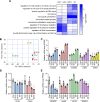
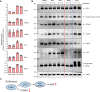
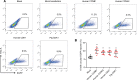
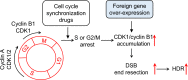
Results: We used various types of cell cycle inhibitors to synchronize the cell cycle in S and G2/M phases in order to investigate their effect on regulating CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HDR. Our results indicated that the four small molecules-docetaxel, irinotecan, nocodazole and mitomycin C-promoted CRISPR/Cas9-mediated KI with different homologous donor types in various animal cells. Moreover, the small molecule inhibitors enhanced KI in animal embryos. Molecular analysis identified common signal pathways activated during crosstalk between cell cycle and DNA repair. Synchronization of the cell cycle in the S and G2/M phases results in CDK1/CCNB1 protein accumulation, which can initiate the HDR process by activating HDR factors to facilitate effective end resection of CRISPR-cleaved double-strand breaks. We have demonstrated that augmenting protein levels of factors associated with the cell cycle via overexpression can facilitate KI in animal cells, consistent with the effect of small molecules.
Conclusion: Small molecules that induce cell cycle synchronization in S and G2/M phases promote CRISPR/Cas9-mediated HDR efficiency in animal cells and embryos. Our research reveals the common molecular mechanisms that bridge cell cycle progression and HDR activity, which will inform further work to use HDR as an effective tool for preparing genetically modified animals or for gene therapy.
Keywords: CCNB1; CDK1; CRISPR/Cas9; Cell cycle; Gene editing; Homology-directed repair.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

