Protective role of IL-17-producing γδ T cells in a laser-induced choroidal neovascularization mouse model
- PMID: 38007487
- PMCID: PMC10676594
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-023-02952-1
Protective role of IL-17-producing γδ T cells in a laser-induced choroidal neovascularization mouse model
Abstract
Background: Vision loss in patients with wet/exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is associated with choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and AMD is the leading cause of irreversible vision impairment in older adults. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) is a component of the microenvironment associated with some autoimmune diseases. Previous studies have indicated that wet AMD patients have elevated serum IL-17A levels. However, the effect of IL-17A on AMD progression needs to be better understood. We aimed to investigate the role of IL-17A in a laser-induced CNV mouse model.
Methods: We established a laser-induced CNV mouse model in wild-type (WT) and IL-17A-deficient mice and then evaluated the disease severity of these mice by using fluorescence angiography. We performed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) to analyze the levels of IL-17A and to investigate the immune cell populations in the eyes of WT and IL-17A-deficient mice. We used ARPE-19 cells to clarify the effect of IL-17A under oxidative stress.
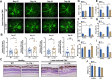
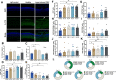
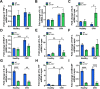
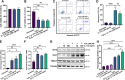
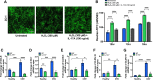
Results: In the laser-induced CNV model, the CNV lesions were larger in IL-17A-deficient mice than in WT mice. The numbers of γδ T cells, CD3+CD4+RORγt+ T cells, Treg cells, and neutrophils were decreased and the number of macrophages was increased in the eyes of IL-17A-deficient mice compared with WT mice. In WT mice, IL-17A-producing γδ T-cell numbers increased in a time-dependent manner from day 7 to 28 after laser injury. IL-6 levels increased and IL-10, IL-24, IL-17F, and GM-CSF levels decreased in the eyes of IL-17A-deficient mice after laser injury. In vitro, IL-17A inhibited apoptosis and induced the expression of the antioxidant protein HO-1 in ARPE-19 cells under oxidative stress conditions. IL-17A facilitated the repair of oxidative stress-induced barrier dysfunction in ARPE-19 cells.
Conclusions: Our findings provide new insight into the protective effect of IL-17A in a laser-induced CNV model and reveal a novel regulatory role of IL-17A-producing γδ T cells in the ocular microenvironment in wet AMD.
Keywords: AMD; Choroidal neovascularization; IL-17A; Inflammation; Oxidative stress.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

