Finite element analysis of the angle range in trans-inferior alveolar nerve implantation at the mandibular second molar
- PMID: 38007495
- PMCID: PMC10676576
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03641-4
Finite element analysis of the angle range in trans-inferior alveolar nerve implantation at the mandibular second molar
Abstract
Background: Trans- inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) implantation technique was wildly used while the potential appropriate angle range in which the residual alveolar bone can bear the stress without absorption are currently unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the stress distribution pattern of the interface between bone and implant by finite element analysis (FEA) to determine the appropriate range of the implant tilt angle.
Methods: Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 120 patients with missing mandibular second molars and vertical bone height < 9 mm in the edentulous area were selected. The distances from the mandibular nerve canal to the buccal cortex, the lingual cortex and the alveolar ridge crest were measured by using a combination of software. The angular ranges of the buccal-lingual inclination of simulated trans-IAN implants were measured and three-dimensional finite element models were constructed in the mandibular second molar area according to the differences of the inclination angles. A vertical load (200N) was then applied to analyze the biomechanical conditions of the implant-bone interface during median occlusion.
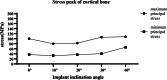
Results: The distance at the second molar from the nerve canal to the buccal cortex, lingual cortex and alveolar crest were 6.861 ± 1.194 mm, 2.843 ± 0.933 mm and 7.944 ± 0.77 mm. Trans-IAN implantation was feasible in 73.33% of patients. The minimum angle and maximum angles of the buccal-lingual inclination of the simulated implant were 19.135 ± 6.721° and 39.282 ± 6.581°. When a vertical static load of 200N was applied, the tensile stress in cortical bone gradually increased with the increase of the implant tilt angle. When the inclination angle reached 30°, the tensile stress (105.9 MPa) exceeded the yield strength (104 MPa) of cortical bone. Compared with the conventional implants, the stress peak value of the vertical ultra-short implant in cortical bone was greater than the stress peak value of the conventional implants at 10°(79.81 MPa) and 20°(82.83 MPa) and was smaller than the stress of the implant at 30°(105.9 MPa) and 40°(107.8 MPa). Therefore, when the bone mass allows, conventional-length implants should be selected whenever possible, and an operative range of the trans-IAN implantation in the mandibular second molar could be retained with an inclination angle of < 30°.
Conclusions: The mandibular nerve canal at the mandibular second molar was obviously biased to the lingual side, which ensured sufficient bone mass at the buccal side. In most patients with severe mandibular atrophy, it was possible to maintain a safe distance from the nerve canal with conventional-length implants via the trans-IAN implantation technique.
Keywords: Finite element analysis; Implant tilt angle; Mandibular atrophy; Mandibular second molar; Trans- inferior alveolar nerve implants.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A CBCT-Based Comparative Study of Alveolar Bone Parameters and Implant Outcomes Among Patients Suffering the Mandibular First and Second Molar Defects.Ann Ital Chir. 2025;96(5):644-653. doi: 10.62713/aic.3951. Ann Ital Chir. 2025. PMID: 40375372
-
[Analysis of the effect of mesial implant position on surrounding bone stress of mandibular edentulous jaw under dynamic loads].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 9;52(11):672-677. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2017.11.005. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29972946 Chinese.
-
Risk assessment of inferior alveolar nerve injury for immediate implant placement in the posterior mandible: a virtual implant placement study.J Dent. 2014 Mar;42(3):263-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Jan 3. J Dent. 2014. PMID: 24394585
-
The Anatomy of the Mandibular Incisive Canal and Its Influence in Implant Therapy: A Scoping Review.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2024 Nov 15;44(6):709-719. doi: 10.11607/prd.6826. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2024. PMID: 38198437
-
The application of CGF combined with GBR in alveolar bone increment for patients with anxiety disorder: A rare case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 10;102(45):e35905. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035905. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37960737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autonomous robotic system-assisted trans-inferior alveolar nerve implantation for patient diagnosed with pemphigoid: a case report.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):1343. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06705-9. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40835940 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Bone Quality, Implant Length, and Loading Timing on Stress Transmission in the Posterior Mandible: A Finite Element Analysis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Aug 20;12(8):888. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12080888. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868400 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of restorative material and connector cross-section area on the stress distribution of fixed partial denture: a finite element analysis.Head Face Med. 2025 Feb 28;21(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13005-025-00484-y. Head Face Med. 2025. PMID: 40022156 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting molar root and periodontal hard tissue changes after orthodontic anterior molar closure of missing tooth spaces retrospective explored based on cone-beam computed tomography three-dimensional reconstruction.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 18;13:e18875. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18875. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40124622 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical behaviour of tilted abutment after fixed partial denture restoration of CAD/CAM materials.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):1128. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04890-7. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39334128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zmysłowska E, et al. Factors affecting mandibular residual ridge resorption in edentulous patients: a preliminary report. Folia Morphol. 2007;66(4):346–352. - PubMed
-
- Felice P, Barausse C, Barone A, et al. Interpositional augmentation technique in the treatment of posterior mandibular atrophies: A retrospective study comparing 129 autogenous and heterologous bone blocks with 2 to 7 years follow-up. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2017;37(4):469–480. doi: 10.11607/prd.2999. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aldelaimi A A K .A Clinical Analysis of Surgically Managed Mandibular Fractures: Epidemiology, Clinical Profile, Patterns, Treatments, and Outcomes. Int Med J 2020(4):27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SKJY2021024/Suzhou Science and Technology Development Plan Projects
- GSWS2022117/Suzhou Health Specially Appointed Talent Research Project
- CXZX202227/Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center
- YJXYYJSDW4/Jiangsu Province Capability Improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education-Jiangsu Provincial Research Hospital Cultivation Unit
- M2021018/Project of Health Commission of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

