Impact of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide on emergency dialysis and prognosis in end-stage renal disease patients with type 4 cardiorenal syndrome
- PMID: 38007545
- PMCID: PMC10676370
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-48125-1
Impact of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide on emergency dialysis and prognosis in end-stage renal disease patients with type 4 cardiorenal syndrome
Abstract
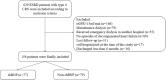
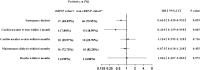
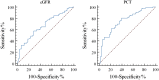
Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide (rhBNP) effects on type 4 cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) and adverse events such as heart failure rehospitalization and all-cause mortality have not been assessed in large-scale research. This study evaluated the impact of rhBNP on emergency dialysis and prognosis in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients with type 4 CRS, and the risk factors of emergency dialysis. This retrospective cohort study included patients with type 4 CRS and ESRD admitted for decompensated heart failure between January 2016 and December 2021. Patients were divided into the rhBNP and non-rhBNP cohorts, according to whether they were prescribed rhBNP. The primary outcomes were emergency dialysis at first admission and cardiovascular events within a month after discharge. A total of 77 patients were included in the rhBNP cohort (49 males and 28 females, median age 67) and 79 in the non-rhBNP cohort (47 males and 32 females, median age 68). After adjusting for age, residual renal function, and primary diseases, Cox regression analysis showed that rhBNP was associated with emergency dialysis (HR = 0.633, 95% CI 0.420-0.953) and cardiovascular events (HR = 0.410, 95% CI 0.159-0.958). In addition, multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (OR = 0.782, 95% CI 0.667-0.917, P = 0.002) and procalcitonin (PCT) levels (OR = 1.788, 95% CI 1.193-2.680, P = 0.005) at the first visit were independent risk factors for emergency dialysis while using rhBNP was a protective factor for emergency dialysis (OR = 0.195, 95% CI 0.084-0.451, P < 0.001). This study suggests that RhBNP can improve cardiac function and reduce the occurrence of emergency dialysis and cardiovascular events in ESRD patients with type 4 CRS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The use of recombinant human B-type natriuretic peptide for the protection of cardiac and renal functions in heart failure patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction in peri-operative period of primary percutaneous coronary intervention].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2010 Nov;22(11):669-73. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2010. PMID: 21122202 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of rhBNP on renal function in STEMI-HF patients with mild renal insufficiency undergoing primary PCI.Heart Vessels. 2016 Apr;31(4):490-8. doi: 10.1007/s00380-015-0642-8. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 25637044 Clinical Trial.
-
[Comparison of the effects of intravenous recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide and nitroglycerin in patients with decompensated acute heart failure: a multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel-design study].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Mar;34(3):222-6. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16630454 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Prognostic Value of Natriuretic Peptide Levels for Adverse Renal Outcomes in Patients With Moderate to Severe Acute Kidney Injury With or Without Heart Failure.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Nov 7;12(21):e031453. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.031453. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37889206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiorenal syndrome in heart failure: a cardiologist's perspective.Can J Cardiol. 2008 Jul;24 Suppl B(Suppl B):25B-9B. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(08)71027-4. Can J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18629386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biobanks in chronic disease management: A comprehensive review of strategies, challenges, and future directions.Heliyon. 2024 May 28;10(11):e32063. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32063. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38868047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The comparative study of the efficacy of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide combined with vasoactive medications for elderly patients with heart failure and hypotension receiving injections.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Mar 15;25(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04609-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40089700 Free PMC article.
-
Attribute based cross classification analyses from the BRIGHTEN study reveal that therapeutic responsiveness to erythropoiesis stimulating agents predicts cardiorenal prognosis in renal anemia.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05762-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603404 Free PMC article.
-
[Anemia and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in adult patients with cardiorenal syndrome: a cross-sectional study].Rev Fac Cien Med Univ Nac Cordoba. 2025 Mar 31;82(1):22-40. doi: 10.31053/1853.0605.v82.n1.44359. Rev Fac Cien Med Univ Nac Cordoba. 2025. PMID: 40163825 Free PMC article. Spanish.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous