Strategies to identify, engineer, and validate antibodies targeting blood-brain barrier receptor-mediated transcytosis systems for CNS drug delivery
- PMID: 38007619
- PMCID: PMC10842915
- DOI: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2286371
Strategies to identify, engineer, and validate antibodies targeting blood-brain barrier receptor-mediated transcytosis systems for CNS drug delivery
Abstract
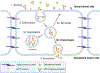
Introduction: Numerous therapeutics for neurological diseases have been developed, but many have failed in clinical trials in part due to limited brain bioavailability, mainly stemming from inefficient transport through the blood-brain barrier (BBB). One potential approach to noninvasive, BBB-targeted drug delivery to the brain is the use of engineered antibodies as delivery vehicles that can transport conjugated drug cargo across the BBB and into the brain via receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT). Effective development of these RMT targeting systems includes novel target discovery, along with antibody engineering and subsequent validation.
Areas covered: This review focuses on both known and emerging RMT systems, targeting antibody properties in relation to BBB trafficking, and antibody validation strategies.
Expert opinion: Clinical development of known RMT targeting systems and identification of novel BBB RMT targets will be complementary strategies for overcoming the BBB in central nervous system (CNS) disease treatment. The search for new RMT targets with higher brain specificity and enriched expression in the brain has given rise to some new targets which may offer unique benefits. It is our opinion that the expansion of BBB RMT system identification, along with targeting molecule engineering and validation strategies, will substantially contribute to the treatment of a wide range of neurological diseases.
Keywords: Receptor-mediated transcytosis; antibody; blood–brain barrier; drug delivery; engineering; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
EV Shusta holds patents for several antibodies with BBB targeting potential.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emerging Technologies for Delivery of Biotherapeutics and Gene Therapy Across the Blood-Brain Barrier.BioDrugs. 2018 Dec;32(6):547-559. doi: 10.1007/s40259-018-0309-y. BioDrugs. 2018. PMID: 30306341 Free PMC article.
-
Smart Strategies for Therapeutic Agent Delivery into Brain across the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020;68(4):316-325. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c19-00854. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 32238649 Review.
-
Antibody screening using a human iPSC-based blood-brain barrier model identifies antibodies that accumulate in the CNS.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):12549-12564. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000851R. Epub 2020 Jul 30. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32960493 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-mediated transcytosis of macromolecules across the blood-brain barrier.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(12):1699-1711. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2255138. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37658673 Review.
-
Transcellular brain drug delivery: A review on recent advancements.Int J Pharm. 2020 Aug 30;586:119582. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119582. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32599130 Review.
Cited by
-
The Glycocalyx: The Importance of Sugar Coating the Blood-Brain Barrier.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8404. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158404. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving the Accuracy of Permeability Data to Gain Predictive Power: Assessing Sources of Variability in Assays Using Cell Monolayers.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Jul 14;14(7):157. doi: 10.3390/membranes14070157. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements and Challenges in Antiamyloid Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2024 Jul 23;2024:2052142. doi: 10.1155/2024/2052142. eCollection 2024. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 39081336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision targeting of the CNS: recent progress in brain-directed nanodrug delivery.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 21;15(32):25910-25928. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03578c. eCollection 2025 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40697447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
