LINC02086 promotes cell viability and inhibits cell apoptosis in breast cancer by sponging miR-6757-5p and up-regulating EPHA2
- PMID: 38008720
- PMCID: PMC10680215
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-023-03245-w
LINC02086 promotes cell viability and inhibits cell apoptosis in breast cancer by sponging miR-6757-5p and up-regulating EPHA2
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are critical regulators in the initiation and progression of breast cancer. Our study aims to characterize the functions of LINC02086 which few published in breast cancer and decipher the downstream molecular mechanisms.
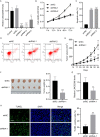
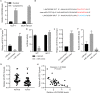
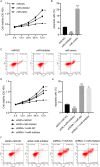
Methods: LINC02086 expression is tested in RNA-seq data from GEPIA database, tumor tissue samples from hospital patients and breast cancer cell lines. LINC02086 was silenced or overexpressed by lenti-virus-mediated shRNAs, or pLVX-Puro plasmids. Luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay were applied to study interactions between LINC02086, miR-6757-5p and ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EPHA2). LINC02086-silencing MCF-7 cells were injected into mice to establish xenograft animal models.
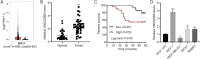
Results: Using RNA-seq data, tumor tissue samples and breast cancer cells, LINC02086 was consistently found to be up-regulated in breast cancer, and correlated with poorer prognosis. LINC02086 knockdown decreased cell viability, promoted cell apoptosis and suppressed tumor growth. LINC02086 interacted with miR-6757-5p that interacted with EPHA2.LINC02086 expression was negatively correlated with miR-6757-5p expression (r = -0.5698, P < 0.001) but was positively correlated with EPHA2 expression (r = 0.5061, P < 0.001). miR-6757-5p expression was negatively correlated with EPHA2 expression (r = -0.5919, P < 0.001). LINC02086 regulated EPHA2 via miR-6757-5p. miR-6757-5p/EPHA2 axis was a mediator of the effect of LINC02086 on cell viability and apoptosis.
Conclusion: LINC02086 increases cell viability and decreases apoptotic cells in breast cancer by sponging miR-6757-5p to upregulate EPHA2. This study presents LINC02086/miR-6757-5p/EPHA2 axis as promising therapeutic targets for breast cancer intervention.
Keywords: Breast cancer; EPHA2; Luciferase reporter assay; RNA pull-down assay; lncRNAs; miRNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA LINC00466 Promotes the Progression of Breast Cancer via miR-4731-5p/EPHA2 Pathway.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(1):120-131. doi: 10.2174/0113892010290582240419051056. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38726776
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00662 promotes proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells via regulating the miR-497-5p/EglN2 axis.Acta Biochim Pol. 2020 Jun 19;67(2):229-237. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5203. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020. PMID: 32558530
-
Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Promotes the Progression of Breast Cancer by Regulating miR-138-5p/ZFX Axis.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2022 Oct;37(8):636-649. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3515. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2022. PMID: 32833504
-
Suppression of long non-coding RNA PCAT19 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion, and increases cell apoptosis through regulation of MELK targeted by miR-142-5p.Genes Genomics. 2020 Nov;42(11):1299-1310. doi: 10.1007/s13258-020-01003-w. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Genes Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32980991
-
Long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1, functioning as a competitive endogenous RNA, upregulates ANXA11 expression by sponging miR-16-5p and promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 14;38(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1188-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 2;41(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02521-z. PMID: 31088485 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
LINC02086 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes malignant phenotypes of pancreatic cancer via miR-342-3p/CA9 axis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Mar 5;24(2):49. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01329-8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38438595
-
Prediction of STAS in lung adenocarcinoma with nodules ≤ 2 cm using machine learning: a multicenter retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13783-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40055661 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative multimodal ultrasound and radiomics for early prediction of neoadjuvant therapy response in breast cancer: a clinical study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):1156. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14556-4. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40629283 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-transcriptomics predicts clinical outcome in systemically untreated breast cancer patients with extensive follow-up.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 15;27(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02061-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40665339 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Nos. 2008085QH410/Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- Nos. KJ2021A0725/Key Project of Natural Science Research in Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province
- Nos. KJ2020ZD49/Major University Science Research Project of Anhui Province
- Nos. S202010367101/Anhui Provincial College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project
- Nos. bydc2022030/College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Bengbu Medical College
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

